Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sample Questions/ Previous year Questions
SecA
1. A ladder, leaning against a wall, makes an angle of 60° with the horizontal. If the foot of the ladder is 2.5 m away from the wall, find the length of the ladder
2. From the top of a 25 m high cliff, the angle of elevation of a tower is found to be equal to the angle of depression of the foot of the tower. Find height of the tower
3. An observer 1.5 m tall is 28.5 m away from a tower of height 30 m. Find the angle of elevation of the top of tower from his eye.
4. The tops of two poles of height 16 m and 12 m are connected by a wire, the wire makes angle of 30° with the horizontal, find length of wire.
SecB
1. The angle of elevation of the top of a hill at the foot of a tower is 60° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the hill is 30°. If height of the tower is 50 m, find the height of the hill.
2. A man standing on the deck of a ship, which is 10 m above water level, observes the angle of elevation of the top of a hill as 60° and the angle of depression of the base of hill as 30°. Find the distance of the hill from the ship and the height of the hill.
3. The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a 50 m high building from the top of a tower are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower and the horizontal distance between the tower and the building, (use √3 = 1.73)
4. There are two poles, one each on either bank of a river, just opposite to each other. One pole is 60 m high. From the top of this pole, the angles of depression of the top and the foot of the other pole are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the width of the river and height of the other pole.
SecC
1. The angle of elevation of a cloud from a point 60 m above the surface of the water of a lake is 30° and the angle of depression of its shadow in water of lake is 60°. Find the height of the cloud from the surface of water.
2. Two points A and B are on the same side of a tower and in the same straight line with its base. The angles of depression of these points from the top of the tower are 60° and 45° respectively. If the height of the tower is 15 m, then find the distance between these points
3. As observed from the top of a 100 m high lighthouse from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45°. If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the lighthouse, find the distance between the two ships. [Use √3 = 1.732]
4. The angle of elevation of a jet plane from a point on the ground is 60°. After a flight of 15 seconds, the angle of elevation changes to 30° If the jet plane is flying at a constant height of 1500√3 m, find the speed of jet plane.
SecD
1. The angle of elevation of a cloud from a point 60 m above a lake is 30° and the angle of depression of the reflection of cloud in the lake is 60°. Find the height of the cloud.
2. A bird is sitting on the top of a 80 m high tree. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the bird is 45°. The bird flies away horizontally in such a way that it remained at a constant height from the ground. After 2 seconds, the angle of elevation of the bird from the same point is 30°. Find the speed of flying of the bird. (Take √3 =1.732)
3. From the top of a 100-meter-high cliff, the angles of depression of two ships on the sea, positioned on the same side of the cliff, are observed to be 30° and 60°, respectively. Find the distance between the two ships, assuming they are on a straight line.
4. A lighthouse is 150 meters tall. From the top of the lighthouse, the angle of depression of a boat is 45°. After 5 minutes, the angle of depression changes to 30° as the boat moves away from the lighthouse. Find the distance traveled by the boat in those 5 minutes
5. An airplane flying at an altitude of 1000 meters observes two landmarks at angles of depression of 30° and 60°, respectively. Find the distance between the two landmarks, assuming both are directly in line with the flight path of the airplane.
Value Based Questions
Problem 1
Situation: An air traffic controller spots two planes flying at the same altitude but at different distances. The first plane is spotted at an angle of elevation of 30° and the second plane at an angle of elevation of 60°. The planes are at an altitude of 500 meters.
1. Calculate the horizontal distance of each plane from the control tower.
2. Why is it important for air traffic controllers to understand the concept of angles and distances using trigonometry?
Problem 2
Situation: A tourist is standing on top of a 50-meter hill and observes two landmarks at different angles of depression. The first landmark is at an angle of depression of 30°, and the second is at 60°.
1. Find the horizontal distance to each landmark.
2. How do concepts like angle of depression and elevation help in making maps and in understanding geographic locations?
Problem 3
Situation: In a rescue operation, a helicopter is positioned 200 meters above the ground. The pilot spots a person stranded on the ground at an angle of depression of 45°.
1. What is the horizontal distance between the helicopter and the stranded person?
2. How does the angle of depression help in rescue operations, and why is it important to understand trigonometric applications in such situations?
Problem 4
Situation: A 15-meter tall building casts a shadow of 25 meters when the sun is at a certain position in the sky.
1. Find the angle of elevation of the sun.
2. How does understanding the concept of angle of elevation help in designing energy-efficient buildings to maximize sunlight?
HOTS
Q1
Two observers A and B are standing on the same side of a tower at distances of 40 meters and 60 meters, respectively. The angle of elevation from A to the top of the tower is 60°, while the angle of elevation from B is 30°.
1. Calculate the height of the tower and the distance between the two observers.
Q2
A ship is sailing directly toward a lighthouse. The angle of elevation of the top of the lighthouse observed from the ship changes from 30° to 45° in 10 minutes. The height of the lighthouse is 100 meters.
1. Calculate the speed of the ship in meters per minute as it approaches the lighthouse.
Q3
A man observes the top of a building from a point on the ground at an angle of elevation of 30°. He then walks 50 meters towards the building and observes the angle of elevation to be 60°.
1. Find the height of the building.
Q4
A balloon is flying at a height of 120 meters. Two people standing at different points on the ground observe the balloon. From the first point, the angle of elevation is 45°, and from the second point, which is 50 meters closer to the balloon, the angle of elevation is 60°.
1. Find the horizontal distance between the first point and the balloon.
Q5
A building and a pole stand on opposite sides of a street. From the top of the building, the angle of depression to the top of the pole is 30° and to the base of the pole is 60°. The height of the building is 20 meters.
1. Find the height of the pole and the width of the street.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Questions
1. The ratio of the height of a tower and length of its shadow on the ground is √3 : 1 what is the angle of elevation of the sun ?
2. A steel wire is tied to the top of an electric pole and the ground making an angle of 60° with the ground. If the height of electric pole is 12 m, then length of steel wire is
3. Height of a tower is 10 m. If the sun’s altitude is 45°, then length of the shadow is :
4. A bridge crossing a river makes an angle of 30° with the river bank. If the length along the bridge from bank to bank is 300 m, then width of river is
5. The angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when it is above the horizontal level is called......
6. Trigonometry was invented because its need arose in.........
7. The angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when it is below the horizontal level is called
8. A tree is broken by the wind, its top struck the ground at an angle of 30° at a distance of 30 m from its foot. The whole height of tree is
9. The angle of elevation of a tower from two points distant l and m (l > m) from its foot and in the same straight line from it are complementary, then the height of the tower is
10. From the top of a tower h metre high, the angle of depression of two objects, which lie on either side of it are a and p. The distance between the two objects is
11. Line joining the eye of an observer to the object viewed by observer is called line of........
12. If the length of the shadow of a tree is √3 times its height, then the angle of elevation is........
13. If the angle of elevation of a tree from a certain distance on the ground is 45°, then the height of tree is equal to...........
14. The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points distant a and b from the base on the same straight line with it are complementary. The height of the tower is........
15. The angle of ........of sun at a given time from a point is called sun’s .....at that time.
16. If the sun’s altitude increases, then the length of shadow of a tower.........
17. A pole is being broken by a storm at one of its point of trisection, then the top struck the ground at an angle of.......
Case Based Questions
Question 1
A helicopter lifts up 1000 feet over an island and spots a swimmer that need to be rescued. Using a distant land mark, the helicopter pilot determines the angle of depression.
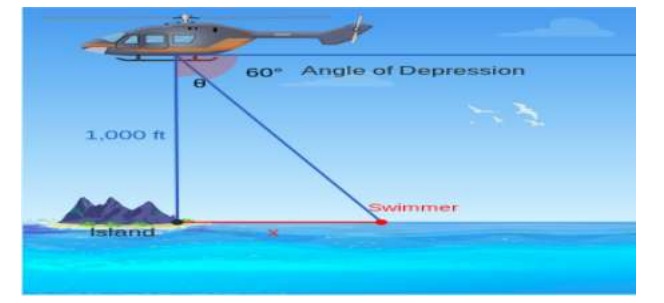
Based on your understanding of the above case study, answer all the five questions below
1. As the angle of depression increases what will be the effect?
2. How does the swimmer’s distance from island changes as the angle of depression is halved from 60° to 30°?
3. For which angle of depression both the helicopter and swimmer’s will be at same distance?
4. Let the swimmer start out 1019 ft. from the island. If he swims half of the distance, what is angle of depression?
5. How would the angle of depression be affected if the helicopter left its initial position and moved vertically upward?
Question 2
We know that during vacation period many people love to go out of the city and gain some experience about historical and scientific values. Keeping in views, Mr.Ramlal decided to go somewhere out of the country and chosen the country USA. In the series of sightseeing, he has first chosen the place sky tower of Mexico City. Then he decided to stand on a building and wanted to see the sky tower. Mr.Ramlal whose height is 2.3 m stood on the top of a building and started to look at the top of sky tower. The horizontal distance between sky tower and the building is 120mt. as shown in the given figure. The angle of elevation of the top and angle of depression of the bottom of the sky tower is 60° and 30° respectively. Looking into the above circumstances try to give the answer of the following questions:
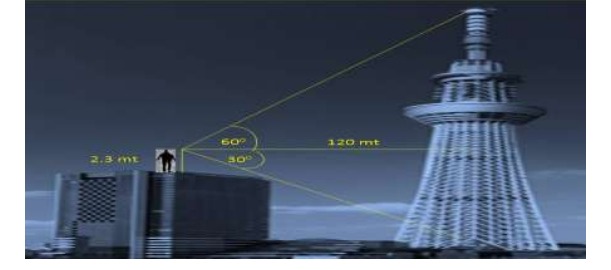
Based on your understanding of the above case study, answer all the five questions below:
1. What is the height of the building excluding the height of Mr. Ramlal standing on it?
2. Find the height of the building including height of Mr. Ramlal?
3. What is the length of line of sight of Mr. Ramlal to the base of the Sky tower?
4. Find the distance from the eye of Mr. Ramlal to top of the sky tower along the line of sight?
5. Find the height of the sky tower?
