Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sample Questions
SecA
1.Which of the following is a zero of the polynomial
(A) 1 (B) -1 (C) 2 (D) None of the above
2.If x=2 is a root of the polynomial
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) -1 (D) 3
3.Which of the following is the degree of the polynomial
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 1
4.The zeroes of the polynomial
(A) -1 and -6 (B) -2 and -3 (C) 1 and 6 (D) 2 and 3
SecB
1.Find the zeroes of the polynomial
2.Factorize the polynomial
3.If p(x)=
4.Verify whether x=1 is a zero of the polynomial
SecC
1.Factorize the polynomial
2.Using the factorization method, solve the quadratic equation
3.Explain the relationship between the coefficients and the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial. Use an example to illustrate.
4.Find the value of kkk if x=3 is a zero of the polynomial
5.Does the polynomial
6.If the zeroes of the polynomial
7.Obtain all other zeroes of
SecD
1.Find the zeroes of the polynomial
2.Given the quadratic polynomial
3.If x=−3 is a root of the polynomial
4.The polynomial
5.Given the polynomial
6. Given that x – √5 is a factor of the polynomial
7. If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) =
8. What must be subtracted from p(x) =
Situation:
A charity organization is collecting funds. The total funds collected are represented by the polynomial
(a) Find the total funds collected after 4 campaigns.
(b) How does the total amount change if the organization runs one more campaign (total of 5 campaigns)?
(c) Explain the importance of running more charity campaigns beyond just the funds collected.
Q1
1.A polynomial p(x) =
Q2
2.The polynomial p(x)=
(a) Find the total cost when 5 units are produced.
(b) If the cost is reduced by reducing the number of units, what does the fact that the polynomial is a perfect square tell you about the cost reduction process?
Q3
3.A quadratic polynomial is given by p(x)=
(a) Factorize the polynomial and explain how you can relate the roots to real-life situations like maximizing profit or minimizing cost.
(b) Discuss the possible outcomes if the polynomial represented the trajectory of an object in motion. How do the zeroes of the polynomial relate to when the object hits the ground?
Q4
4.A polynomial p(x)=
(a) What is the time at which the ball reaches the maximum height?
(b) How would the graph of this polynomial behave if the coefficient of
Questions
1. A quadratic polynomial, whose zeroes are –3 and 4, is
2. Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are √2 and -
3. If the remainder on division of
4. Find the zeroes of the polynomial
5. Can x – 1 be the remainder on division of a polynomial p (x) by 2x + 3? Justify your answer.
6. Is the following statement True or False? Justify your answer. If the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial
7. Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are √2 and
8. Given that two of the zeroes of the cubic polynomial
9. A quadratic polynomial, whose zeroes are –3 and 4, is
Q1
The natural shape of a banana can show the curve of a quadratic polynomial, which is in the form of p(x) =
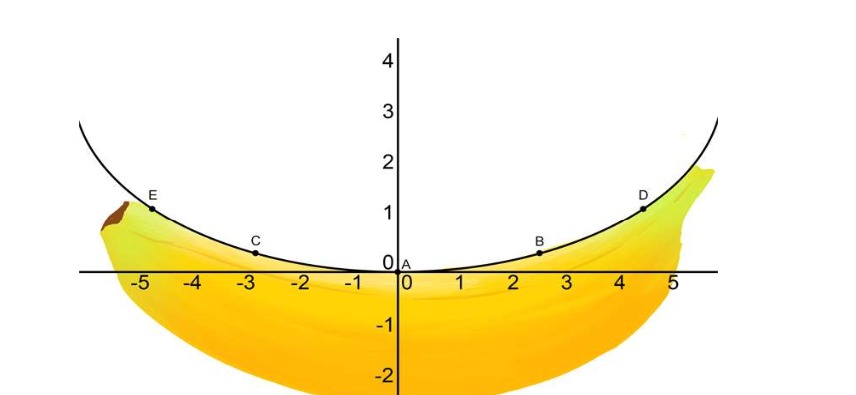
Based on your understanding of the above case study,answer all the five questions below:
(1) The number of zeroes in the polynomial for the shape of the banana is?
(2) If the curve of the banana is represented by the polynomial then the zeroes are?
(3) If the representation of curve of banana whose one zero is 4 and the sum of the zeroes is 0, the quadratic polynomial is?
(4) Each zero of the polynomial is decreased by 2. The resulting polynomial is P(x)=
(5) If the curve representing the polynomial P(x) =
Sol 1
1. 1
2. 0
3.
4. The original polynomial is p(x)=
5. For the polynomial to have equal zeroes, the condition is:
Q2
To transmit a signal, a controller sends it through the horn, and the dish focuses the signal into a relatively narrow beam. When the signal reaches the viewer's house, it is captured by the satellite dish. A satellite dish is just a special kind of antenna designed to focus on a specific broadcast source. The standard dish consists of a parabolic (bowl-shaped) surface and a central feed horn. To transmit a signal, a controller sends it through the horn, and the dish focuses the signal into a relatively narrow beam.
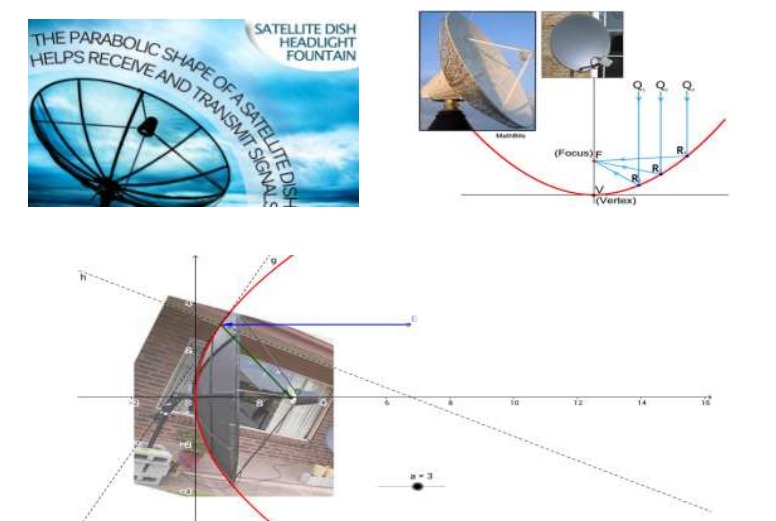
Based on the above figure, answer the following questions:
1. The zeroes of the quadratic polynomial representing the curve of dish are then the polynomial is?
2. If one of the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial representing the curve of the dish of the form P(x)=
3. The number of polynomials having 3 and 7 as zeroes are?
4. If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial P(x)=
5. If the polynomial representing the curve is P(x) =
Sol 2
1. P(x)=
2. The sum of the zeroes is zero, so a =
3. There are infinitely many polynomials that have 3 and 7 as zeroes.
4. The value of p is ±9.
5. One of the factors is (x - 5) or (x +3).
