Exercise 12.1
1. 2 cubes each of volume 64
Solution:
We will find the length of the edge of each cube by using the formula for the volume of a cube =
As the cubes are joined end to end, they will appear as follows:
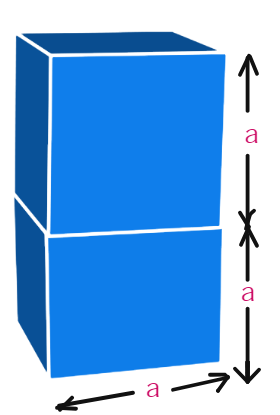
Using the formula for the surface area of a cuboid = 2(
Let the length of the edge of each cube be 'a'
Therefore, volume of the cube =
Volume of the cube,
a = ∛(64
a =
Therefore,
Length of the resulting cuboid, l = a =
Breadth of the resulting cuboid, b = a =
Height of the resulting cuboid, h =
Surface area of the resulting cuboid =
= 2 (
= 2 (
= 2 ×
=
Thus, the surface area of the resulting cuboid is 160
2. A vessel is in the form of a hollow hemisphere mounted by a hollow cylinder. The diameter of the hemisphere is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is 13 cm. Find the inner surface area of the vessel.
Solution:
Let's create a figure of the vessel according to the given description.
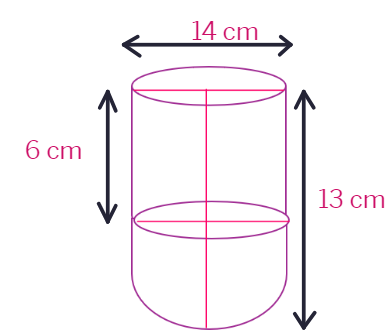
A vessel is in the form of a hollow hemisphere mounted by a hollow cylinder. The diameter of the hemisphere is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is
From the figure it’s clear that the inner surface area of the vessel includes the curved surface area CSA of the hemisphere and the cylinder.
Inner surface area of the vessel = CSA of the
We will find the area of the vessel by using formula:
CSA of the hemisphere = 2π
CSA of the cylinder =
where r and h are the
Diameter of the hemisphere, d =
Radius of the hemisphere, r =
Height of the hemisphere = radius of the hemisphere = r = 7 cm
Radius of the cylinder, r = 7 cm
Height of the cylinder = Total height of the
h =
Inner surface area of the vessel = CSA of the
=
=
= 2 ×
= 2 ×
=
Thus, the inner surface area of the vessel is 572
3. A toy is in the form of a cone of radius 3.5 cm mounted on a hemisphere of same radius.The total height of the toy is 15.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the toy.
Solution:
We can create the figure of the toy as per the given information
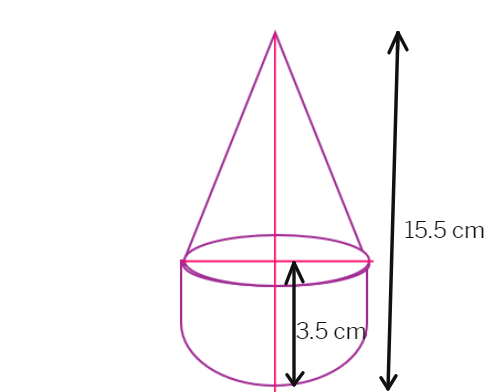
From the figure, it’s clear that the total surface area of the toy includes the curved surface area (CSA) of the cone and hemisphere.
Total surface area of the toy = CSA of the
We will find the total area of the toy by using formula;
CSA of the hemisphere = 2π
CSA of the cone =
Radius of the hemisphere, r =
Height of the hemisphere =
Radius of the cone, r =
Height of the cone = Total height of the
h =
Slant height of the cone, l =
l =
l =
l =
l =
Total surface area of the toy = CSA of the
=
=
=
=
=
=
Thus, the total surface area of the toy is 214.5
4. A cubical block of side 7 cm is surmounted by a hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the surface area of the solid.
Solution:
Given that,
Side of a cube =
To find, the greatest diameter of the hemisphere:
The surface area of the solid.
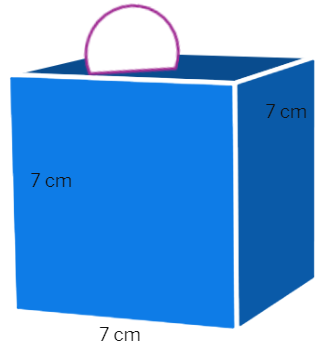
It can be observed from the diagram that the greatest possible diameter of the hemisphere is
Thus the greatest diameter of the hemispherical part=
So the radius of the hemispherical part =
=
Total surface area of the solid = Surface area of cubical part + CSA of
=
= 6
= 6(
=
=
∴ The greatest diameter of the hemisphere is 7 cm and the surface area of the solid is 332.5
5. A hemispherical depression is cut out from one face of a cubical wooden block such that the diameter l of the hemisphere is equal to the edge of the cube. Determine the surface area of the remaining solid.
Solution:
Given that,
Diameter of the hemisphere = Edge of the cube
To determine,
The surface area of the remaining solid.
Radius of the hemisphere =
Total surface area of the solid = Surface area of
=
= 6
= 6
= 6
=
=
∴ The area of the remaining solid is
6. A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder with two hemispheres stuck to each of its ends (see below figure). The length of the entire capsule is 14 mm and the diameter of the capsule is 5 mm. Find its surface area.
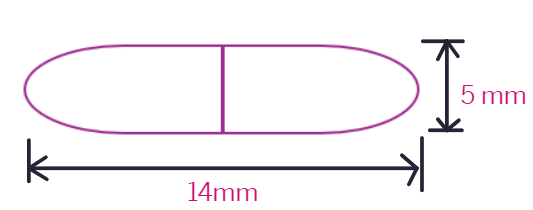
Solution:
Given that,
Length of the entire capsule =
Diameter of the capsule =
To find,
The surface area of the capsule
From the diagram,
Radius of cylindrical part = Radius of
=
=
Length of the cylindrical part (h) = Length of the entire capsule - 2r
=
=
Surface area of capsule = 2 × CSA of
We have: 2 × CSA of hemispherical part =
=
=
Also, CSA of cylindrical part =
=
Surface area of the capsule= 25π + 45π
=
= 70 ×
=
=
∴ The surface area of the capsule is 220
7. A tent is in the shape of a cylinder surmounted by a conical top. If the height and diameter of the cylindrical part are 2.1 m and 4 m respectively, and the slant height of the top is 2.8 m, find the area of the canvas used for making the tent. Also, find the cost of the canvas of the tent at the rate of ` 500 per m2. (Note that the base of the tent will not be covered with canvas.)
Solution:
Given that,
Height of the cylindrical part =
Diameter of the cylindrical part =
Radius of the cylindrical part =
Slant height of conical part =
Cost of 1
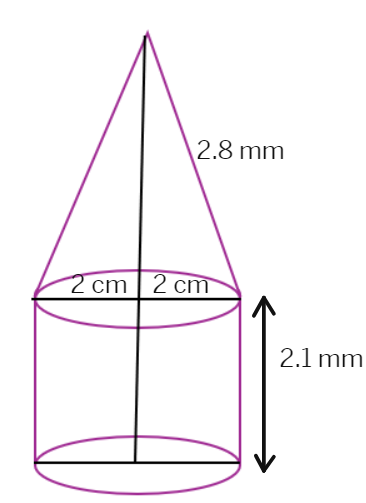
Area of the canvas used = CSA of
=
= (π ×
= 2π(2.8 +
= 2 ×
=
Cost of 1
Cost of canvas =
= Rs.
∴ The cost the canvas that is used to cover the tent is Rs.22,000.
8. From a solid cylinder whose height is 2.4 cm and diameter 1.4 cm, a conical cavity of the same height and same diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest
Solution:
Height of the cylindrical part = Height of the conical part =
Diameter of the cylindrical part = Diameter of the conical part =
To find,
The total surface area of the remaining solid.
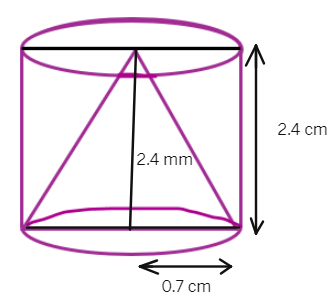
Diameter of the cylindrical part =
Radius of the cylindrical part =
=
Slant height of conical part =
=
=
=
=
The total surface area of the solid = CSA of
=
= (2 ×
= (
=
=
∴ The total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest
9. A wooden article was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a solid cylinder, as shown in below figure. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm, and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the total surface area of the article.
Solution:
Given,
Height of the cylindrical part =
Radius of the cylindrical part = Radius of the hemispherical part =
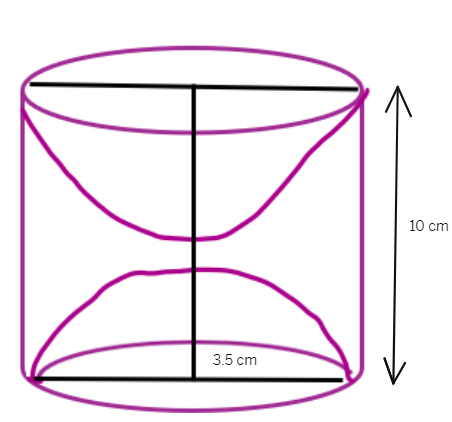
The total surface area of the article =
=
= (2π ×
=
=
= 119 ×
=
∴ The total surface area of the article is 374
