Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
1.Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
2.Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
3.Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
4.Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
SecA
1. The perimeter of a parallelogram is 150 cm. One of its side is greater than the other by 25 cm. Find length of all sides of the parallelogram.
2. Lengths of adjacent sides of a parallelogram is 3 cm and 4 cm. Find its perimeter.
3. In the given figure PR is a diagonal of the parallelogram PQRS.
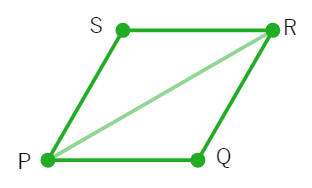
(i) Is PS = RQ? Why?
(ii) Is SR = PQ? Why?
(iii) Is PR = RP? Why?
(iv) Is ΔPSR ≌ ΔRQP? Why?
4. Define a quadrilateral and give an example.
5. What is the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral?
6. In a quadrilateral, if one of the angles is 90° and the other three angles are equal, find the measure of each of the other three angles.
7. Identify the types of quadrilaterals that have opposite sides equal.
8. A quadrilateral has two pairs of parallel sides. What type of quadrilateral is it?
9. Write down the properties of a rectangle.
10. If the sum of two adjacent angles in a quadrilateral is 120°, what is the sum of the other two adjacent angles?
SecB
1. One angle of a parallelogram is of measure 70°. Find the measures of the remaining angles of the parallelogram.
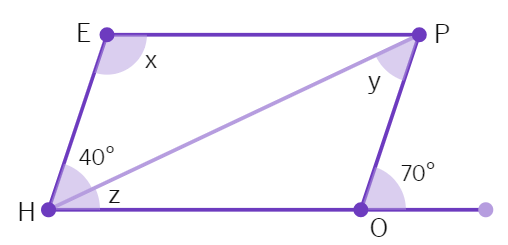
2. The adjacent figure HOPE is a parallelogram. Find the angle measure x, y and z. State the properties you use to find them.
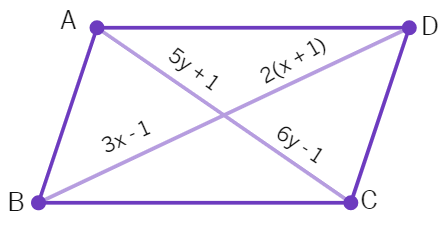
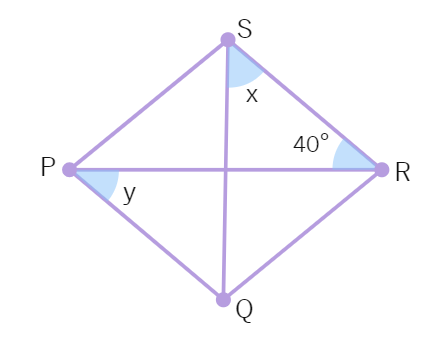
3. Find value of x and y in the following figures.
(i) where ABCD is a parallelogram.
(ii) where PQRS is a rhombus.
4. Find the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral and show how this can be calculated using a triangle
5. If the angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 : 4, find the measure of each angle.
6. A trapezium has one pair of parallel sides. If the parallel sides are of lengths 8 cm and 12 cm, and the height is 5 cm, find the area of the trapezium.
7. Find the length of the diagonal of a rectangle whose length is 12 cm and width is 5 cm.
8. In a rhombus, if the diagonals are 16 cm and 30 cm, find its area.
9. A parallelogram has adjacent sides of lengths 6 cm and 10 cm. If the height corresponding to the base of 6 cm is 4 cm, find the area of the parallelogram.
10. A quadrilateral is cyclic if all its vertices lie on a circle. Can you give an example of a cyclic quadrilateral?
11. Write the properties of a square.
SecC
1. In a parallelogram, the ratio of the adjacent sides is 4 : 5 and its perimeter is 72 cm then, find the sides of the parallelogram.
2. Find the area of a rhombus whose diagonals are 20 cm and 24 cm. Also, calculate the length of each side of the rhombus if one of the diagonals measures 24 cm.
3. The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. If three of the angles are 85°, 95°, and 90°, find the fourth angle.
4. A quadrilateral has the following sides: 8 cm, 15 cm, 12 cm, and 10 cm. If the opposite angles are equal, determine the type of quadrilateral it is.
5. In a trapezium, the lengths of the parallel sides are 8 cm and 12 cm. If the height is 6 cm, find the area of the trapezium.
Sec D
1. A rectangle has a length of 14 cm and a width of 10 cm. Find the diagonal of the rectangle using the Pythagorean theorem. Then, find the area and perimeter of the rectangle.
2. In a trapezium, the parallel sides are of lengths 12 cm and 18 cm. The height of the trapezium is 8 cm. Find the area of the trapezium and explain the steps involved in the calculation.
3. A parallelogram has a base of 10 cm and a height of 6 cm. Calculate the area of the parallelogram. Also, find the length of the diagonals of the parallelogram if one diagonal is twice the length of the other.
4. A cyclic quadrilateral has the following angles: 2x + 10°, 3x - 20°, x + 40°, and 90°. Find the value of x and determine the angles of the quadrilateral.
5. The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular and bisect each other at right angles. If the lengths of the diagonals are 24 cm and 32 cm, find the area of the rhombus and the length of each side.
6. A quadrilateral has the following angles: 80°, 100°, 60°, and 120°. Prove that it is a cyclic quadrilateral and find the sum of its opposite angles.
7. The area of a square is given as 225 cm². Find the length of its side. Then, if one of the diagonals is drawn, find the length of the diagonal and the area of the triangle formed.
Problem 1
An artist is creating a piece of art using different quadrilaterals. She uses a rhombus with each side measuring 5 cm and a height of 4 cm. What is the area of the rhombus? How do artists use mathematical shapes in their creations?
Problem 2
A school is planning to plant trees around a quadrilateral-shaped park. The park is in the shape of a trapezium with the lengths of the parallel sides being 50 meters and 30 meters, and the distance between the parallel sides being 20 meters. How can planting trees around such parks help in maintaining the environment?
Problem 3
Riya wants to decorate her rectangular garden with a fence. The length of her garden is 12 meters and the width is 8 meters. How much fencing material does she need to buy to cover the perimeter of the garden? How can knowing the properties of a rectangle help her in real life?
Q1
The diagonal of a rectangle is thrice its smaller side. Find the ratio of its sides
Q2
A polygon has n sides. Two of its angles are right angles and each of the remaining angles is 144°. Find the value of n.
Q3
In an equiangular polygon, the measure of each exterior angle is 25% of the measure of each interior angle. Find the number of sides.
Select the correct option
Questions
1. The number of diagonals in a polygon of n sides is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
2. The angles of a quadrilateral ABCD taken in an order are in the ratio 3 : 7 : 6 : 4. Then ABCD is a:
(a) kite
(b) parallelogram
(c) rhombus
(d) trapezium
3. In a square ABCD, the diagonals meet at point O. The ∆AOB is:
(a) isosceles right triangle
(b) equilateral triangle
(c) isosceles triangle but not right triangle
(d) scalene right triangle.
4. If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, it will be a:
(a) rhombus
(b) trapezium
(c) rectangle
(d) kite
5. The sides AB and CD of a quadrilateral ABCD are extended to points P and Q respectively. Is ∠ADQ + ∠CBP = ∠A + ∠C? Give reason.
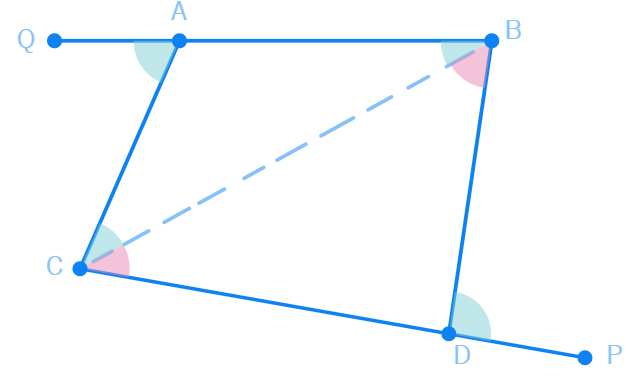
6. The four angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 4 : 5 : 6. Find the angles.
7. In a parallelogram PQRS, the bisectors of ∠P and ∠Q meet at O. Find ∠POQ.
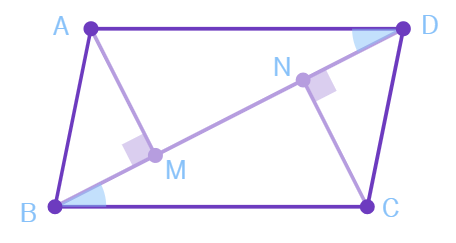
8. If AM and CN are perpendiculars on the diagonal BD of a parallelogram ABCD, Is ∆AMD ≅ ∆CNB? Give reason.
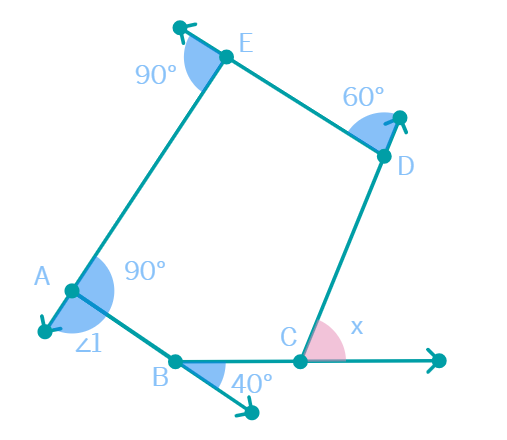
9. Find x in the following figure.
10. The ratio of exterior angle to interior angle of a regular polygon is 1:4. Find the number of sides of the polygon.
Q1
Rahul is planning to design a garden in the shape of a quadrilateral. He plans to include the following features in his garden:
Two opposite sides of the garden are equal in length.
The diagonals of the garden bisect each other at right angles.
The garden will be divided into four equal triangular flowerbeds by the diagonals.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
Questions :
1. Identify the type of quadrilateral Rahul is designing.
2. If the diagonals of the quadrilateral are 8 m and 6 m, find the area of the garden.
3. Name one real-life example where a quadrilateral with these properties is used.
Sol 1
1. Rahul is designing a rhombus, as the diagonals of the quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, and opposite sides are equal in length.
2. Area of the Garden :
The area of a rhombus is given by: Area =
Substituting
The area of the garden is 24 square meters.
3. Real-Life Example
A diamond-shaped field or kite is a real-life example of a rhombus.
Q2
A school playground is designed in the shape of a quadrilateral with the following features:
It has exactly one pair of opposite sides parallel.
The lengths of the parallel sides are 20 m and 12 m.
The distance between the parallel sides (height) is 8 m.
Questions
1. Identify the type of quadrilateral representing the playground.
2. Calculate the area of the playground.
3. If a jogging track is built along the boundary of the playground, find the perimeter of the playground if the non-parallel sides measure 10 m each.
Sol 2
1. Type of Quadrilateral
The playground is in the shape of a trapezium, as it has exactly one pair of opposite sides parallel.
2. Area of the Playground
The area of a trapezium is given by: Area =
Substituting a = 20m, b = 12m, and h = 8m: Area =
The area of the playground is 128 square meters.
3. Perimeter of the Playground
The perimeter of the trapezium is the sum of all its sides: Perimeter = a + b + c + d
Substituting a = 20m, b = 12m, and c = d = 10m : Perimeter = 20 + 12 + 10 + 10 = 52m
The perimeter of the playground is 52 meters.
