Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
1. Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
2. Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
3. Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
4. Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
SecA
1. Pick up the rational numbers from the following given numbers:
2. Write two such rational numbers whose multiplicative inverse is same as they are.
3. The property represented by a + b = b + a is:
(a) closure property
(b) additive identity
(c) associative property
(d) commutative property
4. Which of the following is not true?
(a) Rational numbers are closed under multiplication
(b) Rational numbers are closed under division
(c) Rational numbers are closed under addition
(d) Rational numbers are closed under subtraction
5. What properties, the following expressions show?
(i)
(ii)
6. The property represented by a × (b + c) = a × b + a × c is:
(a) closure property
(b) distributive property
(c) associative property
(d) commutative property
7. The numerical expression:
(a) Addition of rational numbers is not commutative
(b) Rational numbers are not closed under addition
(c) Rational numbers are closed under multiplication
(d) Rational numbers are closed under addition
8. Which of the following statements is correct:
(i) -5 + 3 ≠ 3 + (-5)
(ii)
(iii) 2 is not a natural number
(iv) 17 is not a prime number
(a) Option (iii)
(b) Option (ii)
(c) Option (iv)
(d) Option (i)
SecB
1. Simplify the following expression:
2. Find the sum and difference of the rational numbers
3. Represent the rational number
4. Check whether the rational number
5. Find the product of
SecC
1. If the cost of 4
2. If a car travels
3. If
4. A box contains
5. Solve the following:
Sec D
1.A group of friends equally shared a cake that weighs
2. An elevator descends
3. If the sum of two rational numbers is
Problem 1
During a study group session, 6 students share
Problem 2
A community service group collected
Problem 3
Rohan and Meera were given an assignment to simplify rational numbers. Rohan finds the solution to be
Q1
A group of friends shared a pizza. Two of the friends each ate
Q2
In a marathon race, a runner consumes
Questions
1. Which of the following is not true?
(a) 23 + 54 = 54 + 23
(b) 23 − 54 = 54 − 23
(c) 23 × 54 = 54 × 23
(d) 23 ÷ 54 = 23 × 45
2. Multiplicative inverse of
(a) 1
(b) −1
(c) 0
(d) not defined
3. Three rational numbers lying between
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
In examples 4 and 5 , fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
4. The product of a non-zero rational number and its reciprocal is .
5. If x =
6. True/False: Every rational number has a reciprocal.
7. True/False:
8. Find
9. Using appropriate properties, find
10. The product of two rational numbers is –7. If one of the number is –10, find the other.
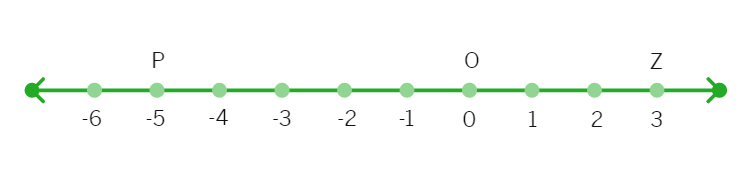
11. Let O, P and Z represent the numbers 0, 3 and -5 respectively on the number line. Points Q, R and S are between O and P such that OQ = QR = RS = SP. What are the rational numbers represented by the points Q, R and S. Next choose a point T between Z and O so that ZT = TO. Which rational number does T represent?
12. A farmer has a field of area of 49
13. Why is
14. Explain why
15. Determine which is larger:
16. Identify the rational number which is different from the other three : 2/3, −4/5, 1/2, 1/3. Explain your reasoning.
17. Find the rational numbers between
18. Find multiplicative inverse of:
19. If
Q1
Sanmesh who is working in a multinational company earns Rs. 150000 per month. Out of his earnings he spend
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(i) How much money did he spend on the food items?
(ii) How much money did he spend on the shopping?
(iii) Calculate the amount spend by Sanmesh on education of children.
Sol 1
Solution:
Sanmesh's monthly earnings: Rs. 150,000
(i) Expenditure on Food Items:
Amount spent on food items =
(ii) Expenditure on Shopping:
Amount spent on shopping =
(iii) Expenditure on Education of Children:
Remaining amount = Total earnings - (Amount spent on food items + Amount spent on shopping) = 150,000 − (15,000 + 37,500) = 150,000 − 52,500 = 97,500
Now, calculate how much Sanmesh spent on education of his children, which is
Amount spent on education =
So,
(i) Sanmesh spent Rs. 15,000 on food items.
(ii) Sanmesh spent Rs. 37,500 on shopping.
(iii) Sanmesh spent Rs. 19,500 on the education of his children.
Q2
A school receives a donation of Rs. 15,000 to purchase classroom supplies. The funds are allocated as follows:
(a) How much money is spent on stationery items ?
(b) What is the amount allocated for educational games ?
(c) Calculate the expenditure on art supplies.
(d) How much money is spent on purchasing books ?
Sol 2
Solution: Given:
Total donation received = Rs. 15,000
(a)
Allocation for stationery items =
So, Rs. 5,000 is spent on stationery items.
(b)
Remaining after stationery items = Rs. 15,000 - Rs. 5,000 = Rs. 10,000
Allocation for educational games =
So, Rs. 2,000 is allocated for educational games.
(c)
Remaining after educational games = Rs. 10,000 - Rs. 2,000 = Rs. 8,000
Allocation for art supplies =
So, Rs. 2,000 is spent on art supplies.
(d)
Remaining after art supplies = Rs. 8,000 - Rs. 2,000 = Rs. 6,000
Therefore, Rs. 6,000 is spent on purchasing books.
Q3
Three friends Rajeev, Sarita and Rahul go to purchase some sweets, namkin and cold drinks for a party. The following chart shows the price and available stock of sweets and namkin in the shop.
| S No. | Sweets and Namkin | Available Stock | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Laddu | 15 kg | Rs. 350 per Kg |
| 2 | Jalebi | 8 kg | Rs. 400 per Kg |
| 3 | Barfi | 4 kg | Rs. 400 per Kg |
| 4 | Mixture | 60 packets | Rs. 40 per packet |
| 5 | Potato chips | 21 packets | Rs. 60 per packet |
| 6 | Cold Drinks | 42 bottles | Rs. 35 per bottle |
| 7 | Dry Fruits (Roasted) | 18 kg | Rs. 980 per Kg |
(a) After purchasing 500gm of sweet laddu, jalebi and barfi each, Rajeev had Rs. 150 left with him. How much money does Rajeev had before the purchase?
(b) Rajeev wants to purchase one packet of Mixture and two packets of potato chips with the remaining Rs. 150. Explain whether he can purchase it or not.
(c) Rahul had Rs. 200 and wants to purchase one packet of Mixture, one packet of potato chips, 250gm Sweet laddu and one bottle of cold drink. But due to insufficient money he had to reduce the quantity of one of the item. Find out the name of that item along with reason.
(d) Sarita had Rs. 250 and wants to purchase those items which were not purchased by her friends. Choose the correct list of items she will purchase.
(i) Jalebi
(ii) (Roasted) Dry fruits
(iii) Barfi
(iv) Potato chips
Sol 3
Solution:
(a) Rajeev spent on sweets as follows:
Laddu: 500g at Rs. 350 per kg
Jalebi: 500g at Rs. 400 per kg
Barfi: 500g at Rs. 400 per kg
Total cost = (500g ×
Given that Rajeev had Rs. 150 left after these purchases, his initial amount of money was:
Initial amount = Total cost + Remaining money = Rs. 575 + Rs. 150 = Rs. 725
So, Rajeev initially had Rs. 725.
(b) The cost for one packet of mixture and two packets of potato chips:
Mixture: Rs. 40 per packet
Potato chips: Rs. 60 per packet
Total cost = Rs. 40 + 2 × Rs. 60 = 40 + 120 = Rs. 160
Since Rajeev only has Rs. 150 left, he cannot afford these items.
(c) Rahul wants to buy:
Mixture: 1 packet (Rs. 40)
Potato chips: 1 packet Rs. 60
Laddu: 250g at Rs. 350 per kg = Rs
Cold drink: 1 bottle (Rs. 35)
Total cost = 40 + 60 + 175 + 35 = Rs. 310
Since Rahul has only Rs. 200, he needs to reduce the quantity of one item. The item he would reduce is the Sweet Laddu because it costs Rs. 175, which is higher than the cost of other items.
(d) Sarita has Rs. 250 and wants to buy items not purchased by her friends:
Items not purchased: Jalebi, Roasted Dry Fruits, Barfi
Comparing the prices:
Jalebi: Rs. 400 per kg
Roasted Dry Fruits: Rs. 980 per kg
Barfi: Rs. 400 per kg
Considering affordability with Rs. 250:
Jalebi (250g): 250g at Rs. 400 per kg = Rs.
So, the correct list of items Sarita will purchase is: (i) Jalebi
Thus, Sarita will purchase Jalebi.
