Extra Curriculum Support
Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
1.Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
2.Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
3.Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
4.Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sec A
1. In the figure given below, the measure of y is.

(a) 30° (b) 120° (c) 130° (d) 150°
2. The measure of angle x, in the given figure is.

(a) 45° (b) 30° (c) 60° (d) 35°
3. In the following figure, the relation between the angles 1, 2 and 3 is.

(a) ∠3 = ∠1 - ∠2
(b) ∠3 + ∠1 = ∠2
(c) ∠3 = ∠1 + ∠2
(d) ∠3 + ∠2 = ∠1
Sec B
1. What is the measure of complement of each of the following angle?
(a) 45° (b) 54° (c) 65°
2. How many angles are formed when 2 lines intersect?
3. If RO is perpendicular to PT, find the measure of angles 1 and 2 in the figure below:

Sec C
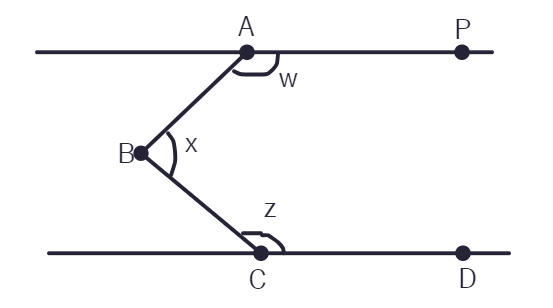
1. From the figure given below, find ∠y and ∠z.

Sec D
1. In the figure below, AP is parallel to CD. Angle PAB (w) is equal to 155° and angle DCB (z) is equal to 117°. Find angle ABC.
Problem 1
A teacher is preparing a geometry lesson for her students and wants to demonstrate the importance of parallel lines and corresponding angles. She uses a real-world example of parallel railway tracks and how the angles between them remain consistent. Explain how understanding angles in real-world scenarios, like railway tracks, helps in designing safe and efficient structures. Why is it important to apply geometric principles practically?
Problem 2
During a construction project, an architect needs to ensure that two adjacent walls meet at a right angle. She uses a protractor to measure and adjust the angle precisely. If the actual angle measured is 89°, how should she adjust it to make sure the angle is exactly 90°? Discuss the significance of precise measurements in construction and how small errors can impact the overall project.
Problem 3
In a school art project, students create geometric patterns using different types of angles. One student decides to use supplementary angles to form various shapes. If she uses an angle of 120°, what is the measure of its supplementary angle? Reflect on how understanding geometric concepts can enhance creativity and problem-solving in art and design projects.
Q1
Two angles are supplementary. The difference between these two angles is 20°. Determine the measures of both angles and verify their relationship using the definition of supplementary angles.
Q2
In the figure, two intersecting lines form four angles at their intersection point. If one of the angles is 35°, determine the measures of all other angles and explain the reasoning using the property of vertically opposite angles.
Q3
Two parallel lines l and m are intersected by a transversal n. If the measure of one of the alternate interior angles is 75°, find the measures of all other angles formed by the transversal with the parallel lines. Explain how you determined these angles using the properties of parallel lines and transversals.
Questions
1. Which of the following pair of angles are supplementary?
(a) 48°, 42° (b) 60°, 60° (c) 75°, 105° (d) 179°, 2°
2. If two lines are intersected by a transversal, then the number of pairs of interior angles on the same side of the transversal is.
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
3. Two lines in a plane which never meet at any point are called .
4. Adjacent angles have a common vertex, a common --- and no-common --- .
5. Sum of two complementary angles is 180°.
6. Sum of two supplementary angles is 180°.
7. Sum of interior angles on the same side of a transversal with two parallel lines is 90°.
8. Out of a pair of complementary angles, one is two-third of the other. Find the angles.
9. The angles between North and West and South and East are.
(a) complementary
(b) supplementary
(c) both are acute
(d) both are obtuse
10. The angles x and 90° – x are.
(a) supplementary
(b) complementary
(c) vertically opposite
(d) making a linear pair
11. In a pair of adjacent angles, (i) vertex is always common, (ii) one arm is always common, and (iii) uncommon arms are always opposite rays Then.
(a) All (i), (ii) and (iii) are true
(b) (iii) is false
(c) (i) is false but (ii) and (iii) are true
(d) (ii) is false
12. One obtuse angle and one acute angle can make a pair of complementary angles.
13. Two supplementary angles are always obtuse angles.
14. Two right angles are always supplementary to each other.
15. One obtuse angle and one acute angle can make a pair of suplementary angles.
16. Interior angles on the same side of a transversal with two distinct parallel lines are complementary angles.
17. An angle is more than 45°. Its complementary angle must be less than 45°.
18. What is the type of other angle of a linear pair if.
(a) one of its angle is acute?
(b) one of its angles is obtuse?
(c) one of its angles is right?
19. If the complement of an angle is 62°, then find its supplement.
20. If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, and the difference of two interior angles on the same side of a transversal is 20°, find the angles.
21. Two angles are making a linear pair. If one of them is one-third of the other, find the angles.
Q1
A railway track consists of two parallel tracks that are connected by cross bars at regular intervals. If a worker standing on one of the tracks observes the cross bars at a certain angle, and the angle between the track and the cross bar is 70°, find the angle formed by the cross bar with the other track. Explain your reasoning using the properties of parallel lines and transversals.
Q2
Two streets, Street A and Street B, intersect at a point forming an angle of 120°. The other two angles formed at the intersection are equal. What are the measures of these two equal angles? Justify your answer using the concept of angles around a point.
Q3
A carpenter is designing a roof structure where two beams intersect at an angle of 90°. He needs to place a supporting beam such that it bisects this right angle. What will be the angle between the supporting beam and each of the original beams? Explain how you arrived at the answer.
Q4
In a classroom, the teacher draws two lines on the board that intersect at an angle of 45°. The students are asked to find the angles formed if one of the lines is extended in both directions. What will be the measures of all the angles formed? Use your knowledge of vertically opposite angles and the angle sum property to solve this.
