Area of a Polygon
When trying to find area of a random polygon, logically, we can simply split the given polygon into smaller familiar geometric shapes and then proceed to find the areas of the individual pieces before adding them up.
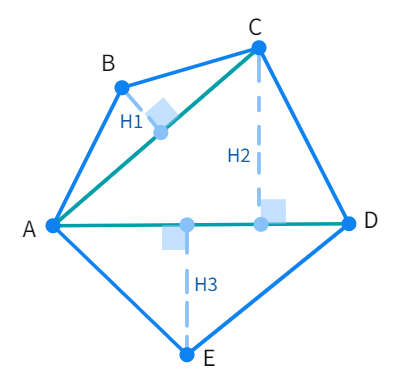
Figure (a)
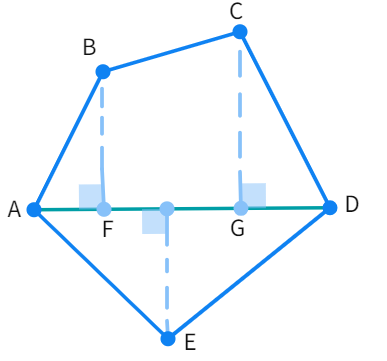
Figure (b)
Above in Figure (a), we can draw the diagonals AC and AD which leads to the polygon being split into three smaller and non-congruent triangles. We can draw their corresponding heights and proceed to calculate the individual areas and add them up
(OR)
we can follow Figure (b), drawing just one diagonal (AD) and getting one trapezium and a triangle. From here on, the process is the same.
Let's Solve
Instructions
Equation blanks: Upon clicking on the blank, you will be provided with a variety of algebraic operations. Use these operations to enter the appropriate answer. For example: To enter perimeter of rectangle, 2(l + b), we need to put '2x(l+b)'. Make sure to use the bracket to be clear about the entities that are getting operated on.
- The area of a trapezium shaped field is 480
m 2
- We know that, the area of a trapezium:
unit 2 - Substituting the values given to us in equation.
- Length of the second parallel side:
m - Thus, we have got the desired value.
Polygon ABCDE is divided into parts. Find its area if:
AD = 8 cm , AH = 6 cm , AG = 4 cm
AF = 3 cm , BF = 2 cm
BF = 2 cm , CH = 3 cm , EG = 2.5 cm
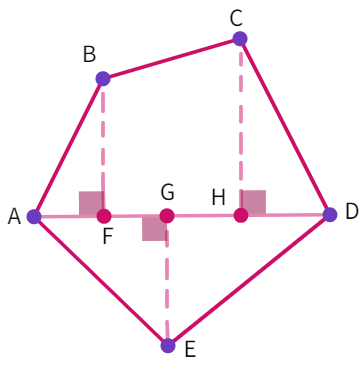
Polygon ABCDE
- We can see from the above figure, that the polygon ABCDE has been divided into 3
and 1 . - The area of a triangle:
where b - base length and h - height length - The area of a trapezium:
where h - height , a and b - the length of the parallel sides. - Finding the individual areas: Area of ABF =
cm 2 cm 2 - Area of ADE =
cm 2 cm 2 - Total area sum:
cm 2 - We got the desired value.
There is a regular hexagon ABCDEF of side 5 cm. Aman and Riddhima divided it in two different ways as indicated in below figures. Find the area using both methods.
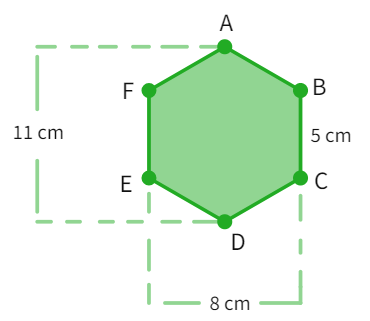
(a) Polygon ABCDEF
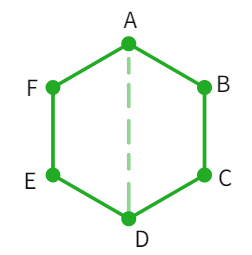
Aman's method
- Upon using the above given dimensions: Height of each trapezium =
cm - Substituting the value we get
- Area of one trapezium:
cm 2 - Area of polygon ABCDEF:
cm 2 - We have found the area using Aman's method.
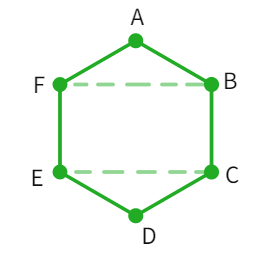
Riddhima's method
- Upon using the above given dimensions: Height of each triangle =
cm - Substituting the value we get
- Area of each triangle:
cm 2 cm 2 - Area of polygon ABCDEF:
cm 2 - We have found the area using Ridhima's method.
Length of the fence of a trapezium shaped field ABCD is 120 m. If BC = 48 m, CD = 17 m and AD = 40 m, find the area of this field. Side AB is perpendicular to the parallel sides AD and BC.
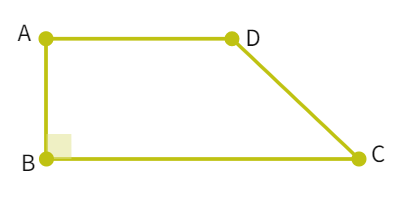
Area of the field
- Using the given data: Length of AB =
m. - Area of trapezium:
where h - height , a and b - the length of the parallel sides. - Substituting the value we get
- Total area of field:
m 2 - We got the respective results.
The diagonals of a rhombus are 7.5 cm and 12 cm. Find its area.
- We know that, Area of rhombus:
where p and q - lengths of the two diagonals. - Substituting the value we get
- Area of rhombus:
cm 2 - We have got the respective result.
Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 5 cm and whose altitude is 4.8 cm. If one of its diagonals is 8 cm long, find the length of the other diagonal.
- We know that a rhombus is a type of
. - We also know, Area of parallelogram:
where b - base length and h - height - Area of rhombus:
cm 2 - Area of rhombus:
where p and q - lengths of the two diagonals. - Substituting the obtained values.
- Length of second diagonal:
cm - We have got the respective result.
The floor of a building consists of 3000 tiles which are rhombus shaped and each of its diagonals are 45 cm and 30 cm in length. Find the total cost of polishing the floor, if the cost per
- We know, Area of rhombus:
where p and q - lengths of the two diagonals. - Substituting the value we get
- Area of each tile:
cm 2 - Area of floor:
m 2 - Thus, cost of polishing the floor: Rs.
- We got the desired result.
Mohan wants to buy a trapezium shaped field. Its side along the river is parallel to and twice the side along the road. If the area of this field is 10500
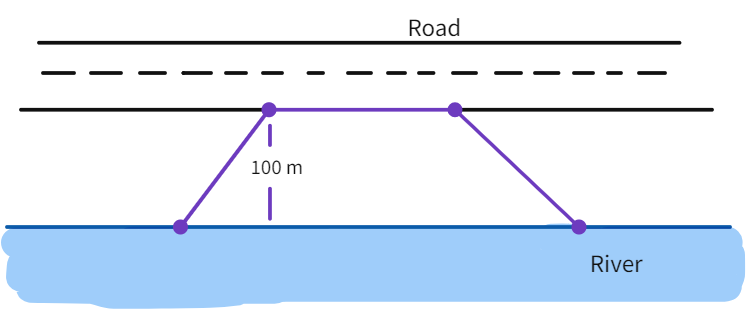
Area of field
- Thus, length along river will be
. - Area of trapezium field:
where h - height , a and b - the length of the parallel sides. - Substituting the value we get
- Value of x:
m - Thus, length along river:
m - We have got the desired result.
Diagram of the adjacent picture frame has outer dimensions = 24 cm × 28 cm and inner dimensions 16 cm × 20 cm. Find the area of each section of the frame, if the width of each section is same.
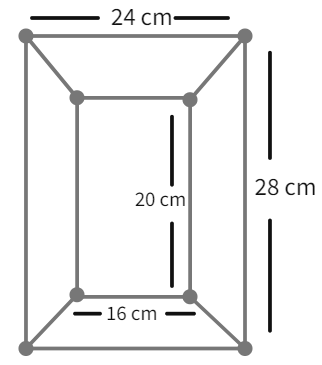
Dimensions of frame
- We observe that the two frames along the length are identical to each other. The same is true for the frames along the breadth.
- Using the given dimensions, the width of the frame:
cm. - Area of each frame:
where h - height , p and q - the length of the parallel sides. - Substituting the value we get
- Area of frame along length:
cm 2 - Area of frame along breadth:
cm 2 - We got the desired result.
