Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sec A
1. If x - 3 is a factor of
(a) 5 (b) -2 (c) -5 (d) 3
2. The zeros of the polynomial p(x) =
(a)
(c)
3. Expand the expression 5(x+2).
4. Factorize: 3x+6.
5. If p=3 and q=4, find the value of pq+p+q.
6. Evaluate the expression 3(2x+5) for x=4.
Sec B
1. If both
2. Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p(x) in case: p(x) =
3. Expand the expression: (x+4)(x−2).
4. Find the value of x if 2x − 5 = 9.
5. Simplify the following expression: 2a + 3b + 4a − 5b.
6. Write the expression for the sum of the square of a number p and twice the number q.
7. Simplify the expression: 6x − 3y + 2x + 5y.
8. Expand and simplify: 2(x+4) + 3 (x−2).
Sec C
1. Simplify: 2(x+3)+4(2x−1).
2. Expand and simplify the expression: 3(x−2)−2(x+5).
3. Find the value of a if 2a+5=15.
4. Expand the binomial expression: (x+2)(x−4).
5. Simplify the expression: 3x(2x−1)−5(x+4).
6. Simplify and factorize:
Sec D
1. Expand and simplify: (x+3)(x+5)+(x−1)(x+2).
2. Solve the equation 3x+4=2x+10 and verify the solution.
3. Find the product of the sum and difference of two terms, x and y, using the identity (x+y)(x−y).
4. If 2x+5y=18, express y in terms of x.
5. Find the value of x and y in the system of equations.
3x+4y=12
2x−5y=1
Problem 1
Riya wants to save money every month for her future education. She starts saving ₹200 every month, but with each passing month, she increases her savings by ₹50. If she continues this pattern for ‘n’ months, express the total savings in terms of ‘n’. How will this disciplined approach help her in achieving her long-term goal?
Problem 2
A school encourages students to recycle plastic bottles. Each student collects 10 bottles in the first week, and in the following weeks, they increase their collection by 5 bottles each week. If the students continue this for ‘n’ weeks, write an algebraic expression for the total number of bottles collected by a student. How does this activity promote environmental sustainability?
Problem 3
In a family, parents save for their children's education. The parents decide to save ₹500 in the first month, and increase the amount by ₹100 every month. Write an algebraic expression to find the total savings after ‘n’ months. How does this consistent saving reflect responsible financial planning for their children's future?
Q1
The cost of producing an item consists of a fixed cost of ₹500 and a variable cost of ₹50 per item produced. If the total cost for producing ‘x’ items is given by an algebraic expression, can you find the expression? Now, if the cost needs to be reduced by 20%, modify the expression accordingly and explain how this impacts large-scale production.
Explore how scaling up production might affect the cost, and analyze the importance of reducing variable costs in a business setting.
Q2
The sum of the areas of two squares is represented by the expression
Analyze how algebraic factoring connects to geometric properties of shapes, and draw conclusions about proportional relationships between the squares.
Q3
You are designing a garden in the shape of a triangle, where the height is 3 units more than the base. The area of the triangle is given by the expression:
Find the base and height if the area is 60 square units. Then, explore how changes in the dimensions of the triangle impact its area, and deduce a strategy for maximizing the garden’s space.
Relate the concept of algebraic expressions to real-life applications in design, showing how algebra helps in optimizing space.
Q4
A business earns a monthly profit, which can be expressed as P(x) =
Examine how algebraic expressions model real-world business scenarios, particularly the role of quadratic expressions in growth analysis.
Questions
Simplify:
(i)
(ii)
The product of a monomial and a binomial is a:
(a) monomial (b) binomial
(c) trinomial (d) none of these
The sum of –7pq and 2pq is:
(a) –9pq (b) 9pq (c) 5pq (d) – 5pq
If we subtract
(a)
Which of the following is a binomial?
(a) 7 × a + a (b)
(c) 4a × 3b × 2c (d)
Sum of a – b + ab, b + c – bc and c – a – ac is:
(a) 2c + ab – ac – bc (b) 2c – ab – ac – bc
(c) 2c + ab + ac + bc (d) 2c – ab + ac + bc
Product of the following monomials
(a)
Product of
(a)
(c)
Which of the following are like terms?
(a)
(c)
Common factor of 17abc,
(a) 17abc (b) 17ab (c) 17ac (d)
Fill the blank: The product of two terms with like signs is a ? term.
Fill the blank: The product of two terms with unlike signs is a ? term.
True or False: Common factor of
Write the greatest common factor in each of the following terms.
(i)
(iii) 2xy,
(v)
(vii)
(viii)
(ix)
(x)
Add:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
Subtract:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
Multiply the following:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi) abc, (bc + ca)
(vii) 7pqr, (p – q + r)
(viii)
(ix) (p + 6), (q – 7)
Q1
A video game is being designed where the player has to throw fruits from the top of a tower into a basket and collect points for each fruit which is successfully collected. The designer has to calculate the distance travelled by the fruit and accordingly display the fruit with respect to time. This depends on factors like the initial speed of the fruit, gravity, air friction, etc. The game designer chose to ignore air friction but take gravity into account. The gravitational force makes the speed of the fruit increase as it comes down and hence the time taken to travel a given distance continues to reduce as the fruit comes down. The distance travelled by a fruit, which is thrown at a speed of 5 m/s after an elapse of time t, is represented by the following algebraic expression:
Distance s =
(1) One of the methods to calculate the time taken by the fruits for travelling a distance s, is to factorise the expression
(2) (i) How much distance would the fruits have travelled after 1 second?
(a) 30 metres (b) 10 metres
(c) 20 metres (d) 5 metres
(ii) As the game level increases, additional challenges are added. The basket disappears and reappears every alternate second, as shown below.
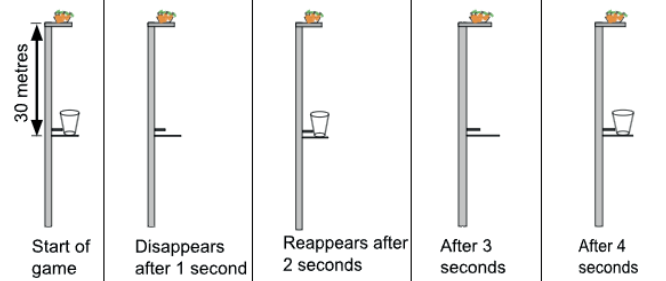
While playing, the player cannot control when the basket should appear, as it will disappear and reappear every alternate second. But before starting the game, she can decide at what distance from the top the basket should be placed. Since the basket continues to disappear every alternate second, it may or may not be available to catch the fruit when a fruit passes through the region where the basket is placed. If the basket catches the fruit, then it is a success and the player wins; if it doesn’t catch the fruit, then it is a failure. Where should the player place the basket before starting the game in order to win? Select all the correct options from below.
(a) Anywhere at a distance of less than 10 metres from the top
(b) 10 to 29 metres
(c) 31 to 59 metres
(d) 61 to 99 metre
Sol 1
Solution:
(1) t = 2sec
(2) (i) Option (b)
(ii) Option (a) and (d)
Q2
A road transport company gave the dimensions of various containers to the fruit seller, Raman. Raman wants to maximise the number of fruit boxes he can ship in one trip of the truck. Raman got 3 different sizes from a box vendor. The vendor told him that as the height of the box increases, so does the size of the base. This provides stability to tall boxes. Raman noticed a pattern in the sizes and figured that the volume of each type of box can be represented by the following polynomial function:
V =
where x is an integer representing half of the height of the box.
Note that each of the three sides of the box is being measured in feet and hence the volume is expressed in cubic feet (
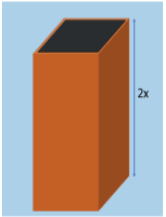
1. Which of the following represents the area of the base of the boxes?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
2. (i) Two factors of the polynomial that represents the area of the base of the boxes are in the form (x + a) and (x + b). Write down the values of a and b.
(ii) Depending on the value of x, the actual dimensions of the box may vary. However, some properties will remain the same, independent of the value of x. If the factors of the algebraic function representing the base of the boxes (deduced in the previous question) represent two sides of the box, then which of the following properties is true about the sides of the base? Select all which are true and note them in the space provided. Assume that each box is at least 2 feet tall and all the lengths are whole numbers.
(a) The difference between the lengths of adjacent sides will be 1 ft
(b) The smallest possible value for the shorter side is 3 ft
(c) The difference between the lengths of adjacent sides will be 2 ft
(d) The smallest possible value for the longer side is 4 ft
3. A box has six faces. We may call them top, bottom and side walls (4 of them).
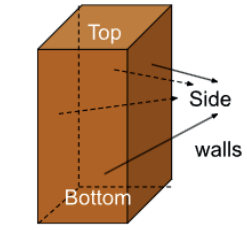
(i) For the boxes that Raman is looking at, which of the following statements are true? More than one statement may be true.
(a) Base will always be a rectangle and never a square
(b) Base will always be a square
(c) Side walls can never be a square
(d) If the height of the box is 6 feet, two out of the four side walls will be a square
(ii) The fruit vendor does not want the boxes to be placed with any of the side walls as the base. If the dimensions of any of the side walls and bottom are the same, the people who load them are likely to get confused. For which of the following boxes are they likely to get confused? The boxes have been referred to using their height.
(a) 12 feet
(b) 6 feet
(c) 9 feet
(d) The dimensions of any of the side walls can never be the same as the bottom
4. If the height of a box is 8 feet, then what is the total area of the floor occupied?
(a) 84
(c) 68
Sol 2
Solution:
1. Option (b)
2. (i) a = 2,b = 3
(ii) Option (a), (b) and (d)
3. (i) Option (a) and (d)
(ii) Option (b)
4. Option (b)
Q3
A stage is constructed in a public garden in Sudhamnagar to erect a memorial statue of a freedom fighter from their town. The stage is 6 metres long and 4 metres wide. The local authorities decide to have a border with uniform width on all the four sides. The plan was to have a green border with special plants around the stage to increase its beauty. They allocated an area for the border, which happened to be equal to the total area of the stage.
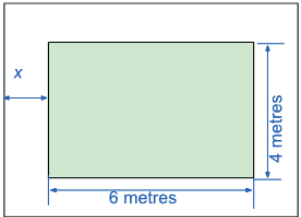
(1) Which of the following correctly represents the area of the stage, including the border?
(a) (6+x) (4+x) = 24 (b) (6+x) (4+x) = 48
(c) (6+2x) (4+2x) = 24 (d) (6+2x) (4+2x) = 48
(2) We can rewrite the correct answer to the previous question by rearranging the terms, as shown below:
Write down the two factors of the polynomial on the left-hand side of the equation.
(3) In order to know the width of the border, we need a value of x. One of the methods to find the value of x is to equate each factor of the polynomial to zero and rearrange the terms. For example, if one of the factors is
Sol 3
Solution:
1. Option (d)
2. (x+6)(x−1)=0
3. We found two possible values for x: x = −6 and x = 1.The width of the border cannot be negative in real-world terms.Therefore, the only valid value for the width of the border is x = 1.
Q4
Algebraic tiles aid students to understand factors of an algebraic expression and also infer the process to identify the factors. As shown in the given below figures, the algebraic tiles kit contains multiple copies of shapes of six different types, each representing a term in the algebraic expression.
1. Blue coloured big square representing
2. Pink coloured big square representing
3. Brown coloured rectangle representing x
4. Pink coloured rectangle representing -x
5. Yellow coloured small square representing the constant 1
6. Pink coloured small square representing the constant -1
The goal is to use as many copies of these 6 types of shapes as required, so as to form a rectangle to represent a given polynomial expression. The factors can be inferred based on the length of the sides of this rectangle.

Foam pieces of 4 different colours cut in 3 different sizes
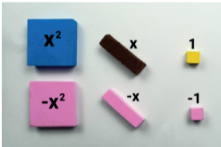
Each size and colour representing a term

Usage of each term to represent expressions

Frame for using algebraic tiles to find factors of a polynomial
(1) Below shows the representation of the polynomial
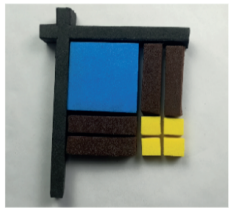
Assertion (A): One xtile and two ‘1’ tiles need to be kept along the horizontal frame. Same is true for the vertical axis.
Reason (R): (x + 2), (x + 2) are the factors of
Which of the following is true?
a. Both A and R are wrong b. A is true, R is wrong c. R is true, A is wrong d. Both A and R are true
(2) Below diagram shows the representation of another expression using the algebraic tiles.
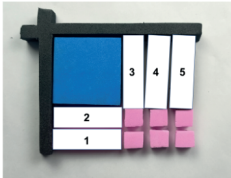
But five blocks have been removed. Select one of the six shapes which should be placed in each position such that the tiles can be used to find the factors of
(Write the name of the tile such as ‘brown coloured rectangle’, ‘pink coloured rectangle', etc. next to the tile number given in the below table.)
| Block Number | Representation |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 |
(3) (i) Among the tiles used to represent
(ii) Compare the area occupied by the tiles for a given value of x to the value of the algebraic expression, which is being represented by the tiles.
(a) Always greater than the value of the expression
(b) Always greater than or equal to the value of the expression
(c) Depends on the algebraic expression
(d) Depends on the value of x
Sol 4
Solution:
(1) Option (d)
(2)
| Block Number | Representation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Pink Coloured rectangle |
| 2 | Pink Coloured rectangle |
| 3 | Black Coloured rectangle |
| 4 | Black Coloured rectangle |
| 5 | Black Coloured rectangle |
(3) (i) 36
(ii) Option (d)
