TriSectional Points of a Line
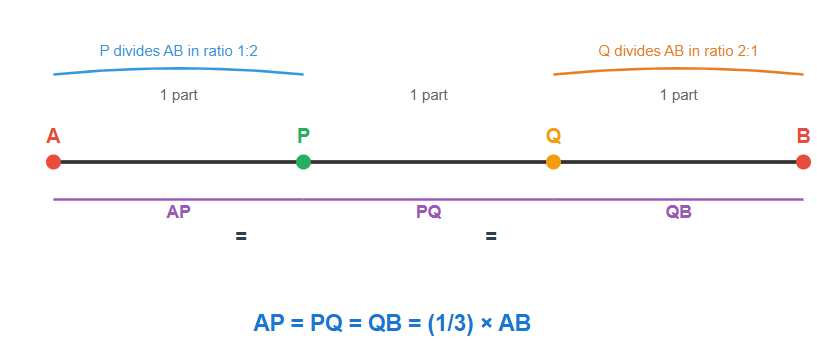
The points which divide a line segment into three equal parts are called trisectional points.
When a line segment is divided by two points into three equal segments, these dividing points are known as points of trisection. If we have a line segment AB with trisectional points P and Q, then AP = PQ = QB.
Finding Trisectional Points Using Section Formula
To find the coordinates of trisectional points, we apply the section formula twice:
(1) The first trisectional point divides the line segment in the ratio
(2) The second trisectional point divides the line segment in the ratio
Let's try it out with a problem:
Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining the points A(2, −2) and B(−7, 4).
Solution:
Let P and Q be the points of trisection of line segment AB, such that AP = PQ = QB.
Step 1: Finding point P
Point P divides AB internally in the ratio 1:2.
Using the section formula:
P(x, y) = (
Where
P(x, y) = (
P(x, y) = (
Step 2: Finding point Q
Point Q divides AB internally in the ratio
Q(x, y) = (
Q(x, y) = (
Thus, the coordinates of the points of trisection are P(−1, 0) and Q(−4, 2).
Trisectional points divide a line segment into
The first trisectional point divides the segment in ratio
The second trisectional point divides the segment in ratio
Both points can be found using the section formula.
8. Find the coordinates of the points of trisection (i.e., points dividing in three equal parts) of the line segment joining the points A(2, – 2) and B(– 7, 4) (Given in the above figure).
Solution : Let P and Q be the points of trisection of AB i.e., AP =
Therefore, P divides AB internally in the ratio 1 : 2.
Therefore, the coordinates of P, by applying the section formula, are:
(
Now, Q also divides AB internally in the ratio 2 : 1. So, the coordinates of Q are:
(
Therefore, the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining A and B are (–1, 0) and (– 4, 2).
Note : We could also have obtained Q by noting that it is the mid-point of PB. So, we could have obtained its coordinates using the mid-point formula.
9. Find the ratio in which the y-axis divides the line segment joining the points (5, – 6) and (–1, – 4). Also find the point of intersection.
Solution : Let the ratio be k : 1. Then by the section formula, the coordinates of the point which divides AB in the ratio k : 1 are
(
This point lies on the y-axis, and we know that on the y-axis the abscissa is
Therefore,
This gives us k =
That is, the ratio is
Putting the value of k = 5, we get the point of intersection as
10. If the points A(6, 1), B(8, 2), C(9, 4) and D(p, 3) are the vertices of a parallelogram, taken in order, find the value of p.
Solution : We know that diagonals of a parallelogram
So, the coordinates of the mid-point of AC = coordinates of the mid-point of BD
(
(
p =
