Geometrical Meaning of the Zeroes of a Polynomial
Geometrical meaning of a zero of a linear polynomial
Why are the zeroes of a polynomial so important?
To understand that, first lets look at the geometrical representation of linear and quadratic polynomials and the geomterical meaning of their zeroes.
When you just look at the equations with x and y, polynomials may appear daunting for some. But polynomials become beautiful when you represent them geometrically. Once you are able to
For example, lets look at the equation y = 2x + 3. What does this mean geometrically? This looks very
But if we substitute different values for x and get y we get multiple points in the co-ordinate system.
Let us try doing the substition of values of
| x | -2 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| y = 2x+3 | -1 | 7 |
When we plot these points in the co-ordinate system we get a graph like below. This makes it much easier to visualize the equation and we can imagine how the different values of x are going to affect y.
Is it better to view polynomials in graph form?
From the graph we can see that the graph of y = 2 x + 3 intersects the x - axis at
You also know that the zero of 2x + 3 is
The graph of y=2x+3 intersects the x-axis in
The linear polynomial ax + b, a
Geometrical meaning of a zero of a quadratic polynomial
Consider the quadratic polynomial
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Now let's plot the graph with these values.
Graph ploting of the quadratic polynomial
From the table above, the zeros of the quadratic polynomial
In fact, for any quadratic polynomial
For any quadratic polynomial, i.e., the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial
From the above examples we observe that there are 3 cases, any quadratic equation will have 0 or 1 or 2 zeroes.
Case(i)The graph cuts x-axis at two distinct points where the x-coordinates are the two zeroes of the quadratic polynomial a
Case(ii)The graph intersects the x-axis at only one point, or at two coincident points. The x-coordinates is the one zero for the quadratic polynomial a
Case(iii)The x-coordinates is the no zero for the quadratic polynomial a
Graphs are given in the below step. Drop each of them into concerned boxes.
So, you can see geometrically that a quadratic polynomial can have either two distinct zeroes or two equal zeroes (i.e., one zero), or no zero. This also means that a polynomial of degree 2 has atmost
Geometrical meaning of a zero of a cubic polynomial
Lets look at some cubic polynomials and plot them to get their geometrical meaning. From that let's try to find some properties.Consider the cubic polynomial
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(i)
We see from the table above that – 2, 0 and 2 are zeroes of the cubic polynomial
Since the curve meets the x-axis in only these 3 points, their x-coordinates are the only zeroes of the polynomial. Let us take a few more examples.
(ii)
Move your mouse over the graph and find the zero polynomial of this graph. This has
(iii)
Move your mouse over the graph and find the zero polynomial of this graph. This has
Note that
We can see that 0 is the x-coordinate of the only point where the graph of y =
Similarly, since
From the examples above, we see that there are at most 3 zeroes for any cubic polynomial. In other words, any polynomial of degree 3 can have at most three zeroes.
Remark : In general, given a polynomial p(x) of degree n, the graph of y = p(x) intersects the x-axis at atmost n points. Therefore, a polynomial p(x) of degree n has at most
Look at the graphs in figure given below. Each is the graph of y = p(x), where p(x) is a polynomial. For each of the graphs, find the number of zeroes of p(x).
Solution :
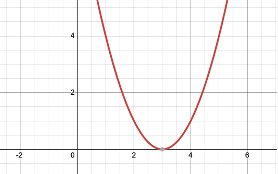
(i) The number of zeroes is
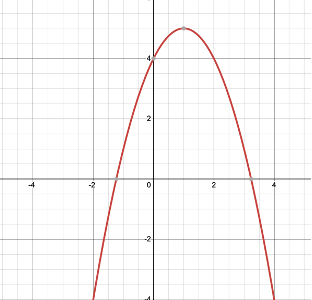
(ii) The number of zeroes is
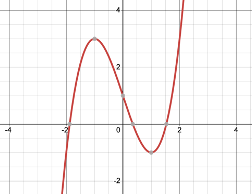
(iii) The number of zeroes is
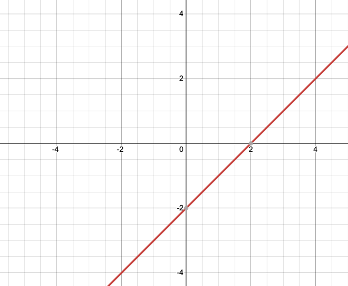
(iv) The number of zeroes is
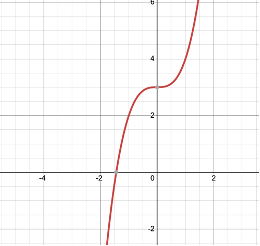
(v) The number of zeroes is
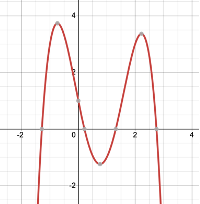
(vi) The number of zeroes is
