Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sample Questions/ Previous year Questions
SecA
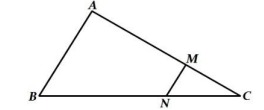
1. In Figure 𝑀𝑁 ∥ 𝐴𝐵, 𝐵𝐶 = 7.5 𝑐𝑚, 𝐴𝑀 = 4 𝑐𝑚 and 𝑀𝐶 = 2 𝑐𝑚. Find the length 𝐵𝑁.
2. In ∆𝐿𝑀𝑁, ∠𝐿 = 50° and ∠𝑁 = 60°. If ∆𝐿𝑀𝑁~∆𝑃𝑄𝑅, then find ∠Q
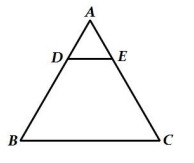
3. In a ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶, 𝐷𝐸 ∥ 𝐵𝐶. If 𝐷𝐸 =
4. In the given figure, 𝐷𝐸 is parallel to 𝐵𝐶 and 𝐴𝐷 = 1 𝑐𝑚, 𝐵𝐷 = 2 𝑐𝑚. What is the ratio of the area of Δ𝐴𝐵𝐶 to the area of Δ𝐴𝐷𝐸?
5. In ∆DEW, AB || EW. If AD = 4 cm, DE = 12 cm and DW = 24 cm, then find the value of DB.
6. The lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus are 24 cm and 32 cm. Calculate the length of the altitude of the rhombus.
7. If ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR, perimeter of ∆ABC = 32 cm, perimeter of ∆PQR = 48 cm and PR = 6 cm, then find the length of AC.
8. If ∆ABC ~ ∆RPQ, AB = 3 cm, BC = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm, RP = 6 cm and PQ = 10, then find QR.
9. A 6.5 m long ladder is placed against a wall such that its foot is at a distance of 2.5 m from the wall. Find the height of the wall where the top of the ladder touches it.
SecB
1. E is a point on the side AD produced of a parallelogram ABCD and BE intersects CD at F. Show that ΔABE~ΔCFB
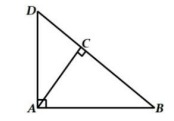
2. In Figure, ∆𝐴𝐵𝐷 is a right triangle, right-angled at 𝐴 and 𝐴𝐶 ⊥ 𝐵𝐷. Prove that
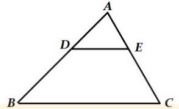
3. In the figure given below, 𝐷𝐸 ∥ 𝐵𝐶. If 𝐴𝐷 = 2.4 𝑐𝑚,𝐷𝐵 = 3.6 𝑐𝑚 and 𝐴𝐶 = 5 𝑐𝑚 Find 𝐴𝐸.
4. A vertical pole of length 6 m casts a shadow 4 m long on the ground and at the same time a tower casts a shadow 28 m long. Find the height of the tower.
5. The sides AB and AC and the perimeter P, of ∆ABC are respectively three times the corresponding sides DE and DF and the perimeter P, of ∆DEF. Are the two triangles similar? If yes, find ar(△ABC)ar(△DEF)
6. If the areas of two similar triangles are equal, prove that they are congruent.
7. The sides of two similar triangles are in the ratio 7 : 10. Find the ratio of areas of these triangles.
SecC
1. In ∆ABC, right-angled at A,BL and CM are the two medians. Prove that 4(
2. In Figure, AD ⊥ BC and BD =
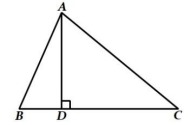
3. In Figure, ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 is right angled at 𝐵. 𝐷 and 𝐸 trisect 𝐵𝐶. Prove that 8
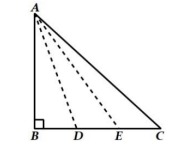
4. In Figure, two triangles ABC and DBC lie on the same side of base BC. P is a point on 𝐵𝐶 such that PQ ∥ BA and PR ∥ BD. Prove that QR ∥ AD.
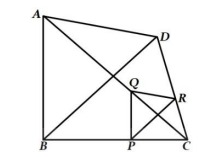
5. In Fig.,
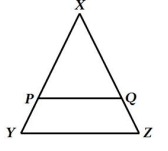
6. In the fig., ABC and AMP are right angled at B and M respectively. Prove that CA × MP = PA × BC.
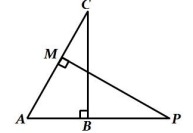
7. In an equilateral ΔABC, D is a point on side BC such that BD = (
SecD
1. If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, prove that the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
In Figure PQ || AB and AQ || CB. Prove that
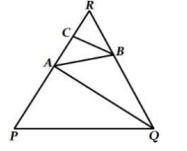
2. Prove that the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of their corresponding sides.The area of the equilateral triangle described on the side of a square is half the area of the equilateral triangle described on its diagonal.
3. Prove that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Use the above theorem, in the following. If 𝐴𝐵𝐶 is an equilateral triangle with 𝐴𝐷 ⊥ 𝐵𝐶, then
4. Prove that the ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides. The areas of two similar triangles are 81
5. State and prove converse of Pythagoras theorem. Using the above theorem, solve the following: In ∆ABC, AB = 6√3 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 12 cm, find ∠B.
6. In a ∆ABC, the perpendicular from A on the side BC of a AABC intersects BC at D such that DB = 3 CD. Prove that 2
7. Hypotenuse of a right triangle is 25 cm and out of the remaining two sides, one is longer than the other by 5 cm. Find the lengths of the other two sides.
Value Based Questions
Problem1
Ramesh measures two sides of the triangle as 6 meters and 8 meters. He wants to know the length of the third side to confirm if the triangle can be a right triangle. Calculate the length of the third side and verify if the triangle is a right triangle.
Problem2
Situation: A farmer wants to fence a triangular piece of land.
The lengths of the sides of the triangular land are 7 meters, 24 meters, and 25 meters. Calculate the area of the triangular land.
Problem3
Situation: Priya notices that her shadow and the shadow of a tree are forming similar triangles on the ground.
If Priya's height is 1.6 meters and her shadow is 2 meters long, while the tree's shadow is 10 meters long, find the height of the tree.
Problem4
Situation: Neha is trying to create an art piece using a triangle and wants to ensure her angles are correct.
Neha has drawn two angles of a triangle as 45 degrees and 55 degrees. What should be the measure of the third angle?
HOTS
Q1
1. If one diagonal of a trapezium divides the other diagonal in the ratio 1:3. Prove that one of the parallel sides is three times the other.
2. A triangle has sides of lengths 7 cm, 24 cm, and 25 cm. Determine whether it is a right triangle without using the Pythagorean theorem.
Q2
1. ABCD is a trapezium with AB ‖ DC in which diagonals AC and BD intersect at E and AAED ˜ ABEC. Prove that AD = BC.
2. Explain why the sum of the angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees. Can this be applied to a quadrilateral? Why or why not?
Q3
1.ABC is a triangle. PQ is a line segment intersecting AB in P and AC in Q such that PQ ‖ BC and divides ΔABC into two parts equal in area. Find
2. In a right-angled triangle, the altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse divides the triangle into two smaller triangles. Prove that these two triangles are similar to the original triangle and to each other.
Q4
1. In a triangle ABC, P divides the sides AB such that AP : PB = 1 : 2, Q is a point on AC such that PQ ‖ BC. Find the ratio of the areas of ΔAPQ and trapezium BPQC.
2. Create a problem involving the circumcircle of a triangle, and solve it. For example, if the circumradius of a triangle is 10 cm and one of its sides is 12 cm, find the area of the triangle.
Q5
1. In the given figure, ABC is a triangle in which AB = AC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively, such that AD = AE. Show that the points B, C, E and D are concyclic.
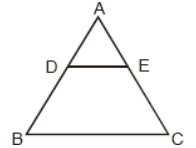
2. Given a triangle ABC where AB = AC, and AD is the median to the base BC. Show that triangle ABD is congruent to triangle ACD.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Questions
1. It is given that ∆DEF ~ ∆RPQ. Is it true to say that ∠D = ∠R and ∠F = ∠P? Why?
2. A and B are respectively the points on the sides PQ and PR of A PQR such that PQ = 12.5 cm, PA = 5 cm, BR = 6 cm and PB = 4 cm. Is 4B||Q/?? Give reasons for your answer.
3. In ∆PQR and ∆MST, ∠P = 55°, ∠Q = 25°, ∠M = 100° and ∠S = 25°. Is ∆QPR ~ ∆TSM? Why?
4. Two sides and the perimeter of one triangle are respectively three times the corresponding sides and the perimeter of the other triangle. Are the two triangles similar? Why?
5. If in two right triangles, one of the acute angles of one triangle is equal to an acute angle of the other triangle, can you say that the two triangles will be similar? Why?
6. The ratio of the corresponding altitudes of two similar triangles is
7. D is a point on side QR of ∆PQR such that PD ⊥ QR. Will it be correct to say that ∆PQD ~ A∆RPD? Why?
8. Find the altitude of an equilateral triangle of side 8 cm.
9. If ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF, AB = 4 cm, DE = 6 cm, EF = 9 cm and FD = 12 cm, find the perimeter of ∆ABC.
10. The lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus are 16 cm and 12 cm. Then, the length of the side of the rhombus is?
11. If ∆ABC ~ ∆EDFand ∆ABC is not similar to ∆DEF, then which of the following is not true?
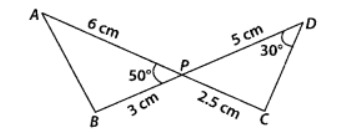
12. In the figure, two line segments AC and BD intersect each other at the point P such that PA = 6 cm, PB = 3 cm, PC = 2.5 cm, PD = 5 cm, ∠APB = 50° and ∠CDP = 30°. Then, ∠ PBA is equal to
13. In ∆ABC and ∆DEF, ∠B = ∠E, ∠F = ∠C and AB = 3 DE. Then, the two triangles are?
14. It is given that ∆ABC ~ ∆DFE, ∠A =30°, ∠C = 50°, AB = 5 cm, AC = 8 cm and DF= 7.5 cm. Then, the following is true:
Case Based Questions
Question 1
Rahul of class X was interested in photography and his friend Amit’s elder brother Sonu was doing wild life photography and he had a powerful camera with zoom lens. Rahul was very keen to know deep about the parts of the camera and met Sonu. Sonu said it was related to application of similar triangles and explained him about Bow tie. Triangle “BOW TIE” mathematics is involved with optics, example- camera lens and eye glasses. Camera does apply to an application of similar triangle which are used on network towers. Photography uses similar triangles to calculate distances from the lens to the object and to the image size.
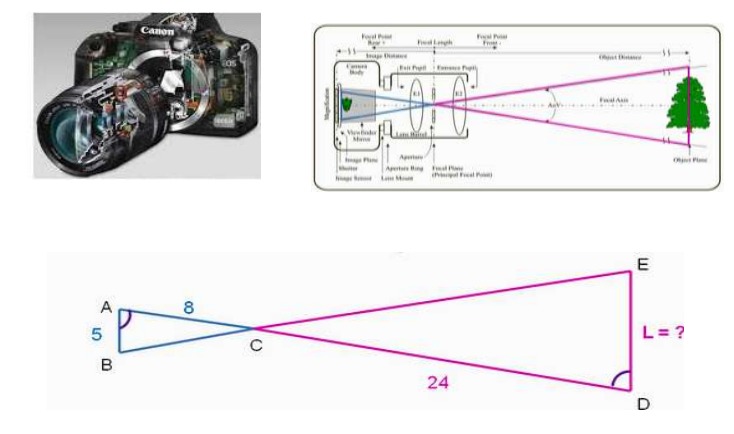
Based on your understanding of the above case study, answer all the five questions below:
1. By what similarity criteria the two triangles formed by the object and image are similar?
2. Suppose in the Bow tie triangle, AB= 5 cm, AC=8 cm, CD = 24 cm, then find ED.
3. The drawing below illustrates the position of the camera and the distance from the lens of the camera to the film is given. The height of the actual sculpture is?
4. In the Bow-Tie triangle, if AC and Then, ∠ABC =
5. If in the Bow-tie triangle ABC and DEC, the length of the object is three times the length of the image. Then the two triangles are
Question 2
Madhu is very particular about her health. She usually goes to a nearby park for jogging. She knows jogging helps to build strong bones, as it is a weight bearing exercise to strengthen muscles improve cardiovascular fitness and burn plenty of kilojoules to help maintain a healthy weight. The park has two similar triangular jogging paths as shown. The dimensions of the inner path are 300m, 350m, 550m.The shortest side of the outer path is 600m

Based on your understanding of the above case study, answer all the five questions below:
1. Find the length of the longest side of the outer path.
2. What can we say about the ratio of the perimeter of inner path to outer path?
3. y which criteria the two triangular paths are similar?
4. The distance along Talbot Road from the Triangle Park entrance to the Walkthrough is 800 yards. The distance along the Talbot Road from the Walkthrough to Clay Road is 1408 yards. The distance along Woodbury Avenue from the walkthrough to Clay Road is 1760 yards. If the walkthrough is parallel to Clay Road. Find the distance from the entrance to the walkthrough along Woodbury
5. If the park is like the figure given below and FG = EG, BE =15cm, CF = 20cm, AE = 9cm, DF = 12cm, then which triangles are similar?
