Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sample Questions/ Previous year Questions
SecA
1. How many right angles do you make if you start facing south and turn clockwise to west?
2. Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 3 to 6.
3. What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn through, when it goes from 12 to 3?
4. What is the angle name for half a revolution?
5. Draw a hexagon and write its sides and diagonals?
6. How many degrees are there in half a revolution ………
7. If an angle is larger than a right angle, but less than a straight angle, it is called an………
8. When two lines intersect and the angle between them is a right angle, then the lines are said to be ………
9. Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in each figure:
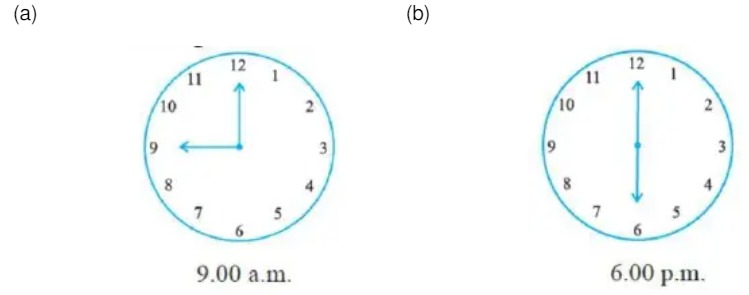
10. What is the name of a three-dimensional shape with six rectangular faces?
SecB
1. Draw a rough sketch of a regular octagon. Draw a rectangle by joining exactly four of the vertices of the octagon.
2. All equilateral triangle are isosceles, but all isosceles triangle are not equilateral. Justify the statement.
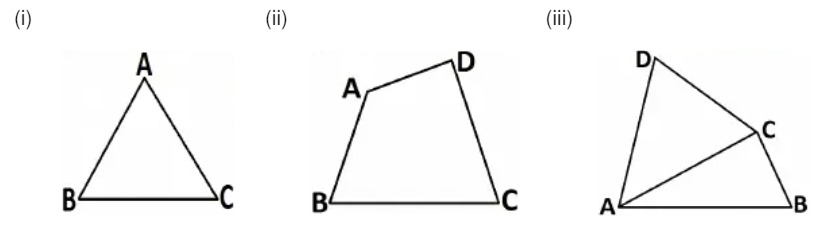
3. How many angles are formed in the figures (i), (ii) and (iii)? Name them.
4. A ship sailing in river Jhelam moves towards east. If it changes to north, through what angle does it turn?
5. Identify the number of edges, vertices, and faces in a cube.
6. What are the differences between a square and a rectangle? Provide at least two differences.
7. Draw a right-angled triangle and mark the right angle. Explain why it is called a right-angled triangle.
8. Define an acute angle and give an example with a diagram.
SecC
1. Measure and classify the angles as acute, obtuse, or right:
2. You are given a square sheet of paper. If you fold it diagonally, what shape do you get? Explain the properties of the new shape formed.
3. You are given a square. If you cut it along its diagonal, what new shapes are formed? Explain the properties of these new shapes.
4. Identify and draw an obtuse triangle. Explain why it is called an obtuse triangle and how it differs from an acute triangle.
5. Draw a line segment AB of length 7 cm. From point A, draw another line segment AC that is perpendicular to AB. Measure and write down the length of AC.
6. Draw a hexagon and label all its sides. Then, explain how a hexagon differs from a pentagon in terms of sides and angles.
SecD
1. Explain with diagrams the difference between a rhombus and a parallelogram. Mention at least two properties that differentiate them.
2. Draw a cylinder and a cone. Write down the number of faces, edges, and vertices for each shape. Explain how a cylinder and a cone are similar and different.
3. A rectangle has a length of 12 cm and a breadth of 8 cm. Draw the rectangle and calculate the perimeter and area of the rectangle.
4. Draw a square and a circle with the same perimeter. Calculate the perimeter of both shapes and explain why the area of the circle is greater than that of the square.
Value Based Questions
Problem1
Situation: You and your friends are playing a board game that involves moving pieces based on the roll of a dice. You notice that one of your friends is not following the rules and is moving their piece more than they should.
How would you address the situation to ensure everyone plays fairly? Why is it important to follow rules, both in games and in life?
Problem2
Situation: While measuring angles for a homework assignment, you realize that you made a mistake in your measurements and got the wrong answer. You are tempted to leave it as is, but you know it’s not correct.
What should you do when you realize you've made a mistake in your work? How does correcting your mistakes help you learn and grow?
Problem3
Situation: During a nature walk, you observe that many leaves, flowers, and other natural objects have shapes similar to the ones you learned in class, like circles, ovals, and hexagons.
How can recognizing shapes in nature help you appreciate the world around you? What does this teach you about the connection between math and the environment?
Problem4
Situation: Your art teacher asks you to draw a picture using only geometric shapes like triangles, circles, and squares. You decide to create a scene from your favorite story using these shapes.
How can you use your creativity to make a detailed and interesting drawing with just basic shapes? Why is creativity an important skill to develop?
HOTS
Q1
1.(a) Draw a regular hexagon and mark a point inside it. Now, reflect the hexagon across a line passing through one of its sides.
2.(b) Does the reflected hexagon coincide with the original hexagon?
Q2
1. (a) Consider a regular pentagon and a regular octagon. Which shape will have more diagonals?
2. (b) Derive a formula to calculate the number of diagonals in any polygon, and then use it to find the number of diagonals in both shapes. Discuss how understanding the properties of polygons can be useful in architectural design.
Q3
1. (a) Draw a trapezium with one pair of parallel sides and mark all the angles.
2. (b) If one of the angles is 60°, can you find the other angles assuming the trapezium is isosceles?
3. (c) Explain how knowing the properties of angles helps in solving problems involving complex shapes.
Q4
1. (a) Consider a protractor, which is a tool used to measure angles. If a protractor is divided into 180 equal parts, explain how you can use it to measure acute, obtuse, and right angles.
2. (b) Discuss how understanding angles is crucial in fields like engineering and carpentry.
Q5
1. (a) Combine different basic shapes like triangles, rectangles, and circles to create a new geometric figure.
2. (b) Describe the new shape you created and explain how the properties of the original shapes contribute to the characteristics of the new figure. How does this exercise relate to creativity in design and problem-solving?
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Questions
1. What is the measure of straight angle?
2. What is complete angle?
3. Find the number of right angle turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from 3 to 6.
4. Draw the rough sketch of the following:
(a) Acute angle
(b) Obtuse angle
(c) Reflex angle
5. What are the degree measures of the following angles?
(a) Right angle
(b) A complete angle
(c) Straight angle
6. Draw two acute angles and one obtuse angle without using a protractor. Estimate the measures of the angles. Measure them with the help of a protractor and see how much accurate is your estimate.
7. What is the measure of – (i) a right angle? (ii) a straight angle?
8. Classify each one of the following given angles as right, straight, acute, obtuse or reflex:
9. What is the main disadvantage of comparing line segments by just mere observation?
10. Why is it a good choice to use a divider rather than a ruler while measuring the length of a line segment?
11. Draw any line segment, say AB. Now, take any point C between A and B. Measure the lengths of – AB, BC and AC. Is AB = AC + CB?
12. If A, B, and C are three points that are present on a line so that AB = 5 cm, BC is equal to 3 cm and AC is equal to 8 cm, which one of these lies between the other two?
13. Draw any five triangles and measure their sides. Check in each and every case if the sum of the length of any two sides is always less than the third side.
14. How many right angles will you make if you start facing
(a) South(S) and turn clockwise to the West(W)?
(b) North(N) and turn anti-clockwise to the East(E)?
(c) West(W) and turn to West(W)?
(d) South(S) and turn to the North(N)?
15. A figure is regular if its all sides are equal in length and all angles are equal in measure. Can you identify a regular quadrilateral?
16. A diagonal is a line segment that will join any of the two vertices of the polygon and is not any side of the polygon. Draw a sketch of a pentagon and also draw its diagonals.
17. State true(T) or false(F)
(i) Each angle of the rectangle is a right angle.
(ii) The opposite sides of a rectangle are always equal in length.
(iii) The diagonals of a square are always perpendicular to one another.
Case Based Questions
Question 1
Classifications of Triangles:
Triangles can be classified on the basis of sides and angles. Type of Triangle on basis of angles
(a) Acute angled triangle: A triangle with all angles are acute
(b) Right triangle: A triangle with one right angle
(c) Obtuse angled triangle: A triangle with one angle is obtuse
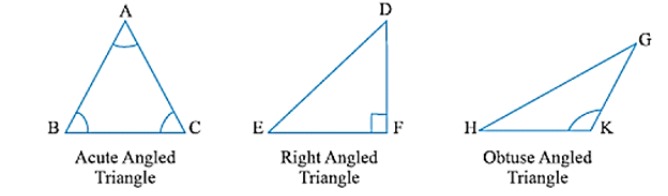
Type of Triangle on basis of sides
(a) Equilateral triangle: A triangle whose all three sides are of equal measure
(b) Isosceles triangle: A triangle whose two sides are of equal measure
(c) Scalene triangle: a triangle whose all sides are of different measure
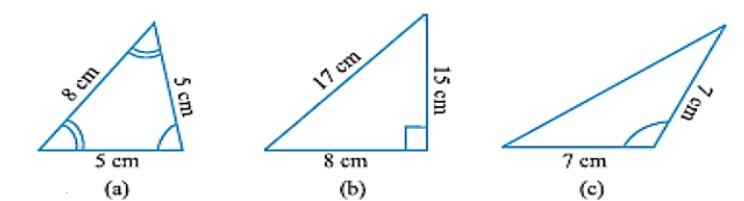
Using above information answer the following:
1. Name the triangle whose all angles are acute
2. Does a obtuse triangle has two right angles
3. Name the triangle whose all sides are of equal measures and also name the triangle whose all angles are acute.
4. In above fig.name triangle (b) in two different ways
Question 2
When two lines intersect and the angle between them is a right angle, then the lines are said to be perpendicular. If a line AB is perpendicular to CD, we write AB ⊥ CD.
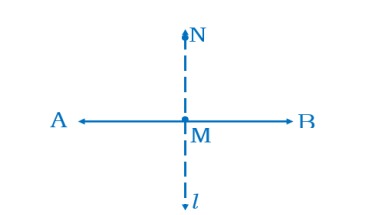
You can give plenty of examples from things around you for perpendicular lines (or line segments). The English alphabet T is one. Is there any other alphabet which illustrates perpendicular?
Based on your understanding of the above case study, answer all the five questions below:
1. In AB ⊥ CD what is the angle between AB and CD?
2. Write two English alphabets which represent perpendicular lines.
3. Is letter V model of perpendicular lines?
