Area
Looking at the closed figures given below, can you tell which figure takes up more space on the flat surface?


In order to check which shape takes up more space, we need to calculate area.
The amount of surface enclosed by a closed figure is called its
So, can you tell, which of the above figures has more area?
It is difficult to do so just by looking at these figures.
So, what can be done?
One way is to place them on top of a squared paper or graph paper where every square measures (1 cm × 1 cm). After tracing an outline of the figure, count the number of squares enclosed by the figure.
Some of them are completely enclosed, some only around half the size, others less than half and so on. This isn't the most accurate way to calculate the area but is good enough to just get an approximate idea.
The area of the figure becomes the number of centimetre squares that are covered by it.
But what about the partially covered squares?
One thing that can be done is to adopt a certain convention, say:
The area of one full square is taken as 1 sq. unit. If it is a centimetre square sheet, then area of one full square will be 1 cm2.
Ignore portions of the area that are less than half a square.
If more than half of a square is in a region, just count it as one square.
If exactly half the square is counted, take its area as
1 2
Find the area of the shape shown in the figure sjown below.
This figure is made up of
Moreover, it is covered by full squares and half squares only. This makes our job simple.
(i) Fully-filled squares =
(ii)Half-filled squares =
Area covered by full squares = 3 × 1 sq units =
Area covered by half-full squares = 3 ×
Total area =
By counting squares, estimate the area of the figure shown below.
Make an outline of the figure on a graph sheet.
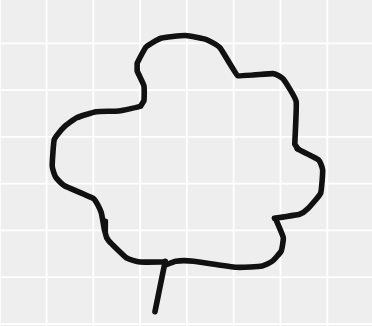
| Covered Area | Number | Area estimate(sq units) |
|---|---|---|
| (i) Fully-filled squared | ||
| (ii) Half-filled squares | ||
| (iii)More than half-filled squared | ||
| (iv)Less than half-filled squares |
Total area = 9 + 2.5 + 8 =
By counting squares, estimate the area of the figure shown below.
Make an outline of the figure on a graph sheet. This is how the squares cover the figure.

| Covered Area | Number | Area estimate(sq units) |
|---|---|---|
| (i) Fully-filled squared | ||
| (ii) Half-filled squares | ||
| (iii)More than half-filled squared | ||
| (iv)Less than half-filled squares |
Total area = 5 + 2 =
Outline the said rectangle on a graph paper having 1 cm × 1 cm squares. The rectangle covers
The area of the rectangle =
The measures of the sides of some of the rectangles are given. Find their areas by placing them on a graph paper and counting the number of square.
| Length | Breadth |
|---|---|
| 3 cm | 4 cm |
| 7 cm | 5 cm |
| 5 cm | 3 cm |
Area of the rectangle:
Area of the rectangle:
Area of the rectangle:
What do we infer from this? Area of a rectangle =
Without using the graph paper, can we find the area of a rectangle whose length is 6 cm and breadth is 4cm ?
1. Find the area of the floor of your classroom.

Taking length as 30 m and breadth as 18 m
Area =
2. Find the area of any one door in your house.

Taking length as 2 m and breadth as 0.5 m
Area =
Let us now consider a square of side 4 cm. What will be its area?
If we trace it on a centimetre graph paper, what do we observe?
It covers
i.e. the area of the square = 16 sq cm = 4 × 4 sq cm.
To find the area of several squares, let’s consider examples with side lengths of 2, 3, and 5 units. We will calculate the area based on the graph by counting the unit squares within each square.
If side-length is 2: Area =
We find that in each case,
Area of the square = side × side
Find the area of a rectangle whose length and breadth are 12 cm and 4 cm respectively.
Length of the rectangle =
Breadth of the rectangle =
Area of the rectangle = 12 cm × 4 cm =
Find the area of a square plot of side 8 m.
Side of the square =
Area of the square = side × side = 8 m × 8 m =
The area of a rectangular piece of cardboard is 36 sq cm and its length is 9 cm. What is the width of the cardboard?
Area of the rectangle =
Length =
Area of a rectangle = length × width
So, width =
Thus, the width of the rectangular cardboard is 4 cm.
Bob wants to cover the floor of a room 3 m wide and 4 m long by squared tiles. If each square tile is of side 0.5 m, then find the number of tiles required to cover the floor of the room.
Now, take the circle drawn on the squared paper (1 square = 1 × 1 cm), what will be the area?
Using the convention, find the area of the circle on the graph paper and also calculate the area using the mathematical formula of Area of circle = πr2 .
Also answer the questions given below:
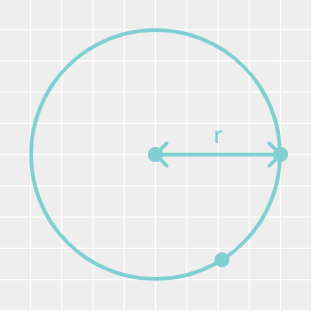
Find area of circle.
Area using square counting:
Area using formula:
Difference between graph paper counting and obtained formula value :
The formula gives a higher value for area.
Calculate the approximate areas of the given figures by checking the number of squares covered (use the above mentioned convention)
Note: In case decimals, round it to one decimal place.
Fill the table and calculate the approximate area of the given curved figure by checking the number of squares (use the usual convention).
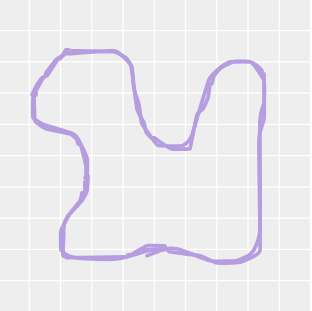
Calculate the estimate area
| Covered Area | Number | Area Estimate (sq units) |
|---|---|---|
| Fully-filled squares | ||
| Half-filled squares | ||
| More than half-filled squares | ||
| Less than half-filled squares | ||
| Total Area | - |
A piece of string is 30 cm long. What will be the length of each side if the string is used to form.
Square Perimeter =
side =
Equilateral triangle Perimeter =
side =
Regular Hexagon Perimeter =
side =
Find the area in square metre of a piece of cloth 1m 25 cm wide and 2 m long.
Length of the cloth =
Breadth of the cloth = 1 m 25 cm = 1 m +
Area of the cloth = length of the cloth × breadth of the cloth
= 2 m × 1.25 m =
