Exercise 6.2
If AB || CD, CD || EF and y : z = 3 : 7, find the value of x.
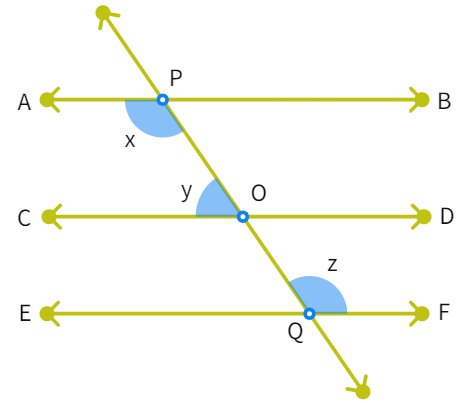
- x and y are angles on the same side of the transversal: x + y =
° - We also have ∠POD =
- (1) as they are corresponding angles. - and y + ∠POD =
° - (2) as a linear pair - (1) and (2) gives us:
+ = 180° - Since, y : z = 3 : 7 we can write 3w + 7w = 180° which gives us w =
° - Upon solving for values using the equations, we get: x =
° , y = ° and z = ° - We have found the answer
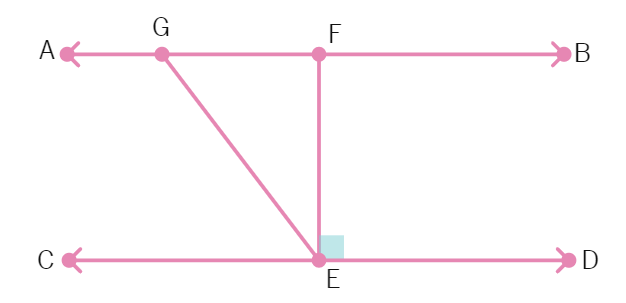
In the given figure, if AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠ GED = 126°, find ∠ AGE, ∠ GEF and ∠ FGE.
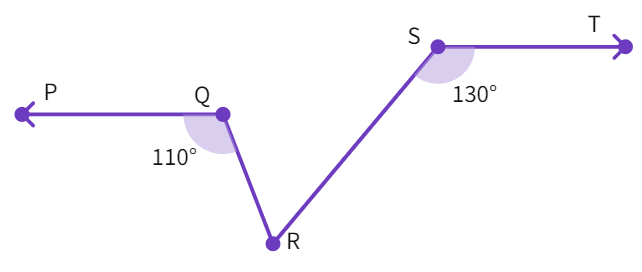
In the figure, if PQ || ST with ∠ PQR = 110° and ∠ RST = 130°, find the value of ∠ QRS.
Lets's construct a line XY parallel to PQ. Now, consider the below figure-
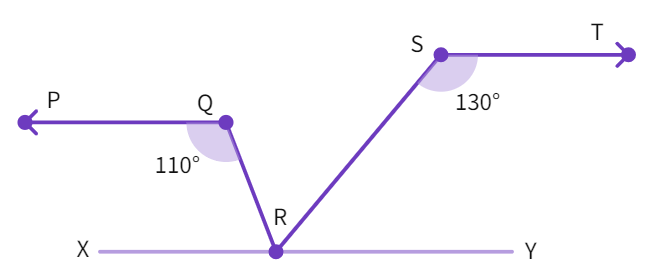
- As angles on the same side of the transversal: ∠PQR + ∠
= 180° - This gives ∠QRX =
° - Similarly, ∠RST + ∠
= 180° - Giving ∠SRY =
° - From the figure, ∠
+ ∠QRS + ∠SRY = 180° - Upon solving, we get: ∠QRS =
° - We have found the answer
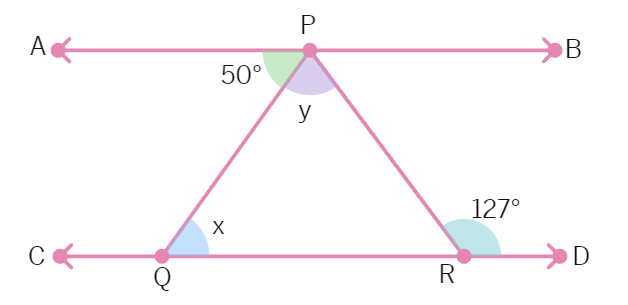
In the figure, if AB || CD, ∠ APQ = 50° and ∠ PRD = 127°, find x and y.
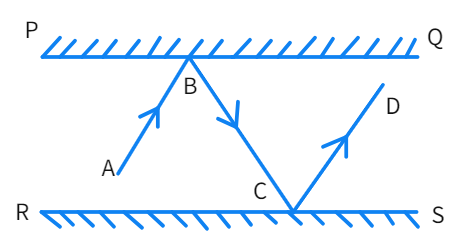
PQ and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray AB strikes the mirror PQ at B, the reflected ray moves along the path BC and strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD. Is AB || CD ?
First, draw two perpendiculars BE and CF, such that BE ⊥ PQ and CF ⊥ RS.
Since PQ || RS, BE || CF as well.
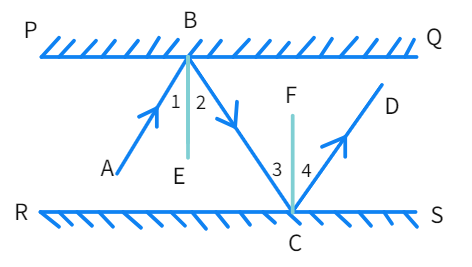
- As Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection, we get: ∠1 = ∠
and ∠ = ∠4 - We also have BE || CF with BC acting as a transverse: ∠2 = ∠
- Since, ∠2 and ∠3 are also equal
- We can further say the above
- Which gives ∠ABC = ∠
- As the alternate interior angles are equal, we can conclude.
