Exercise 13.2
1.Count the number of faces , vertices , and edges of given polyhedra and verify Euler’s formula.
i.
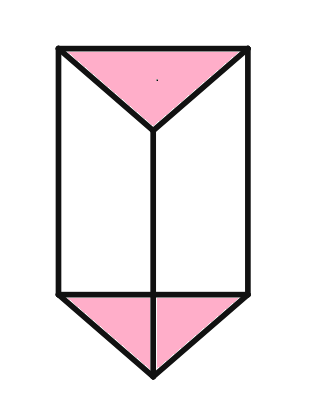
Solution
Triangular Prism Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V =
Plugging in the values:
Therfore Euler's formula is verified for the triangular prism.
ii.
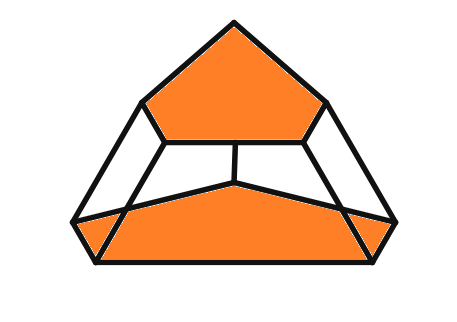
Solution
Polyhedron Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the polyhedron.
iii.
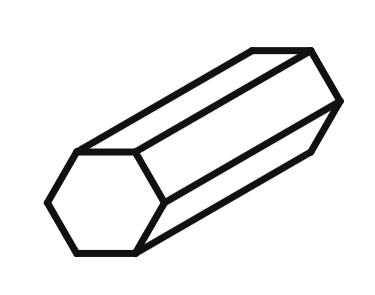
Solution
Hexagonal Prism Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the hexagonal prism.
iv.
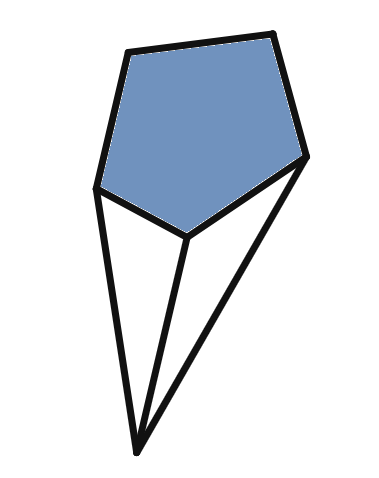
Solution
Polyhedron Analysis
Faces (F):
1 pentagonal face
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the polyhedron.
v.
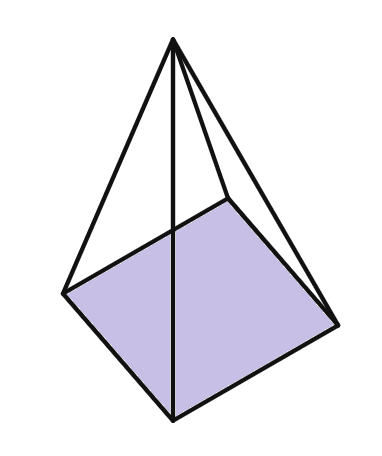
Solution
Polyhedron Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the polyhedron.
vi.
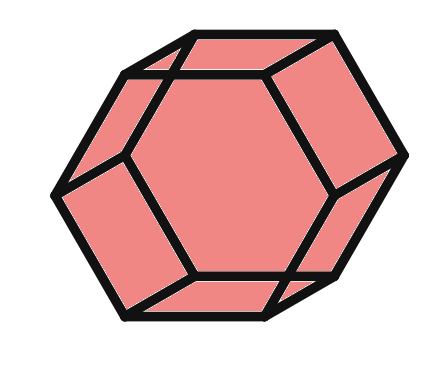
Solution
Polyhedron Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the polyhedron.
vii.
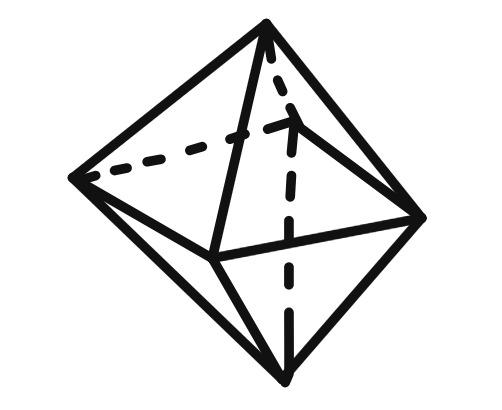
Solution
Polyhedron Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the polyhedron.
viii.
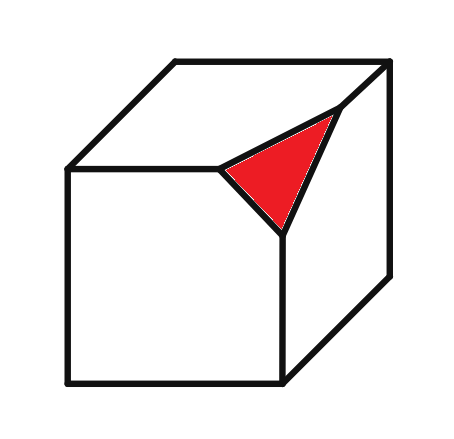
Solution
Polyhedron Analysis
Faces (F):
Vertices (V):
Edges (E):
Euler's Formula Verification
Euler's formula: F - E + V = 2
Plugging in the values:
Therefore Euler's formula is verified for the polyhedron.
2. Is a square prism and cube are same? explain.
Solution
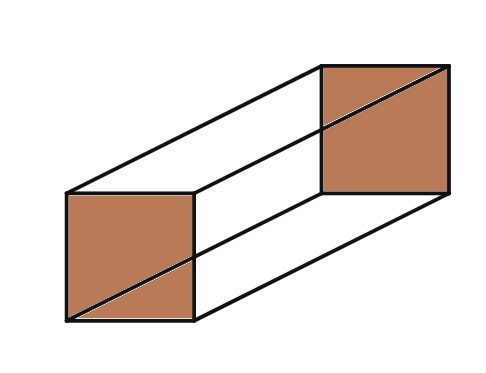
Square Prism Image:
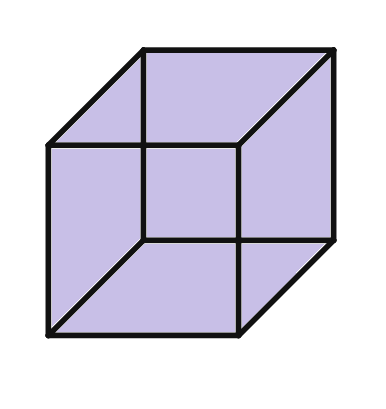
Cube Image:
Is a square prism and cube are same.
Here's why:
Square Prism:
Faces:
Edges:
Vertices:
Shape of Bases:
Shape of Sides:
Cube:
Faces:
Edges:
Vertices:
Shape of Bases:
Shape of Sides:
The main difference lies in the shape of their sides. A square prism has rectangular sides, while a cube has square sides. This means that all edges of a cube are the same length, whereas a square prism can have different lengths for its edges.
3. Can a polyhedra have 3 triangular faces only? explain.
Solution
Can a polyhedra have 3 triangular faces only?
A polyhedron needs at least three faces to meet at each corner to be a 3D shape. If you only have 3 triangles, they can only make a flat triangle or a floppy, open shape, not a closed 3D one. You'd need more faces to make a proper corner.
4. Can a polyhedra have 4 triangular faces only? explain.
Solution
Can a polyhedra have 4 triangular faces only?
Yes! This shape is called a triangular pyramid (or tetrahedron). It has a triangular base and
5. Complete the table by using Euler’s formula.
| Faces (F) | Vertices (V) | Edges (E) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 6 | ? |
| 5 | ? | 9 |
| ? | 12 | 30 |
Solution
Let's break down how we found the missing values:
Row 1: We had F =
Using E = F + V - 2, we get E =
Row 2: We had F =
Using V = 2 + E - F, we get V = 2 +
Row 3: We had V =
Using F = 2 + E - V, we get F = 2 +
Threfore,
| Faces (F) | Vertices (V) | Edges (E) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 6 | |
| 5 | 9 | |
| 12 | 30 |
6. Can a polyhedra have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices?
Solution
Can a polyhedra have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices?
Euler's formula for polyhedra states: F - E + V = 2
Let's plug in the given values:
Since the result is not
7. Complete the following table:
| Object | No. of vertices | No. of edges |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
 | ||
 |
Solution
Explanation:
To find the number of vertices and edges, we carefully examined each 3D shape:
Rectangular Prism:
Vertices (V): Count the corners:
Edges (E): Count the lines:
Square Pyramid:
Vertices (V): Count the corners:
Edges (E): Count the lines:
Triangular Prism:
Vertices (V): Count the corners:
Edges (E): Count the lines:
| Object | No. of vertices | No. of edges |
|---|---|---|
 | 8 | 12 |
 | 5 | 8 |
 | 6 | 9 |
8. Name the 3-D objects or shapes that can be formed from the following nets .
(i).
Solution
(ii).
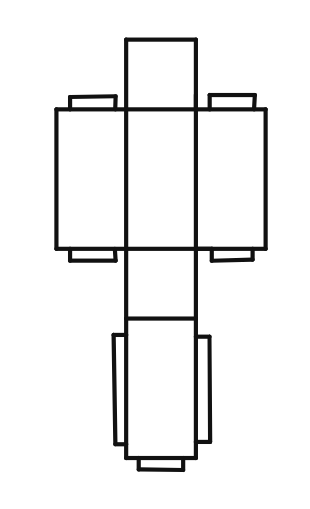
Solution
(iii).
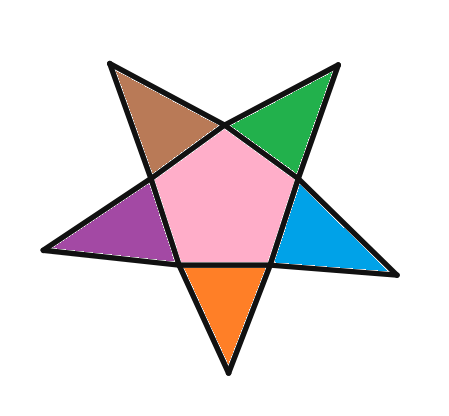
Solution
(vi).
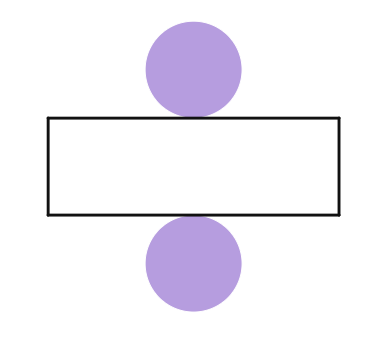
Solution
(v).
Solution
(vi).
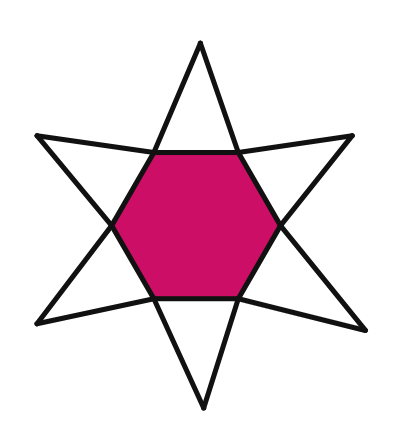
Solution
(vii).
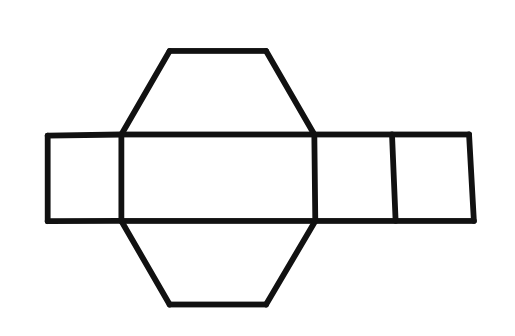
Solution
9 (i). Draw the following diagram on the check ruled book and find out which of the following diagrams makes cube ?
(a).
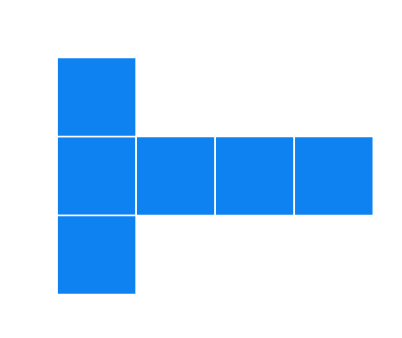
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: The squares are arranged in a straight line and won't create a closed shape when folded.
(b).
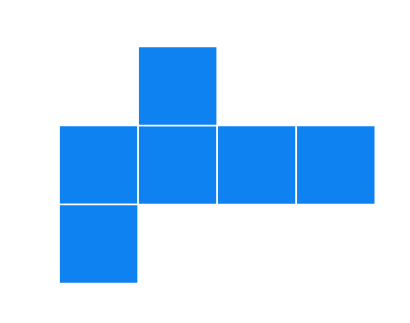
Solution
It can form a cube.
Can form a cube: This is a classic net that forms a cube.
(c).
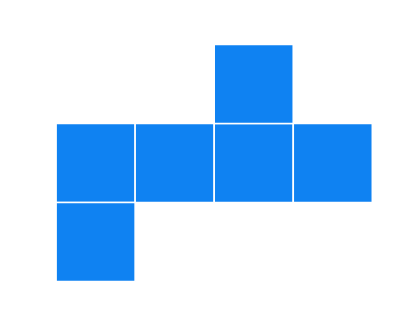
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: When folded, there will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(d).
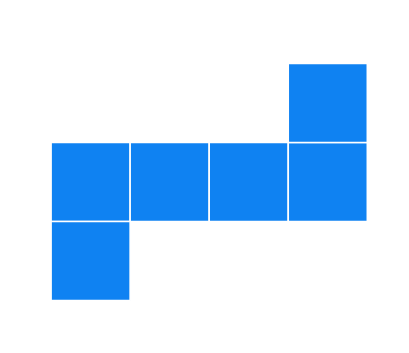
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: There will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(e).
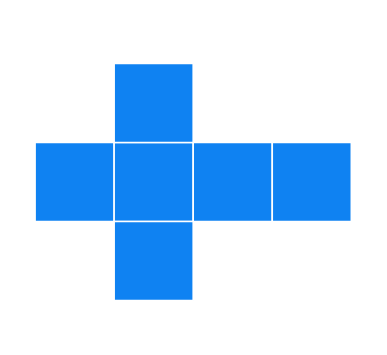
Solution
It can form a cube.
Can form a cube: This is another standard net that forms a cube.
(f).
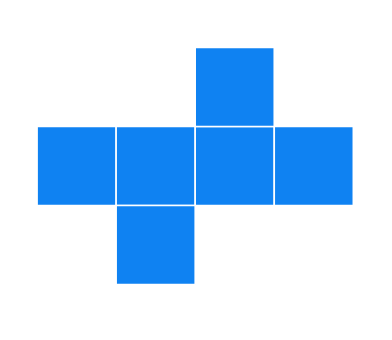
Solution
It can form a cube.
Can form a cube: This is also a valid net for a cube.
(g).
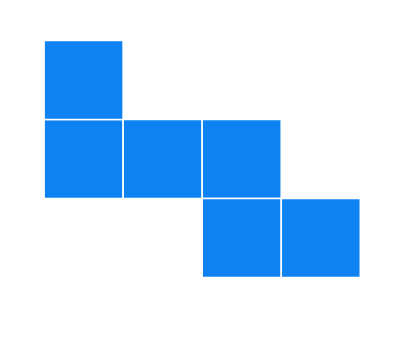
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: When folded, there will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(h).
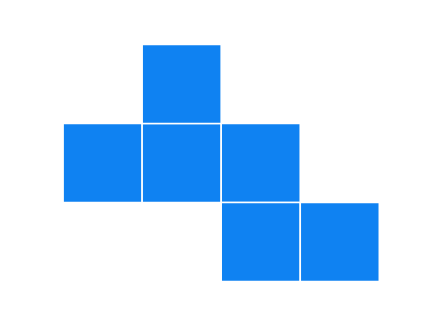
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: When folded, there will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(i).
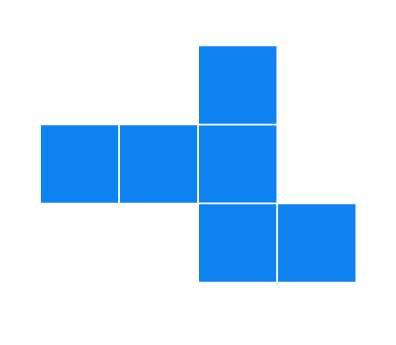
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: When folded, there will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(j).

Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: When folded, there will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(k).
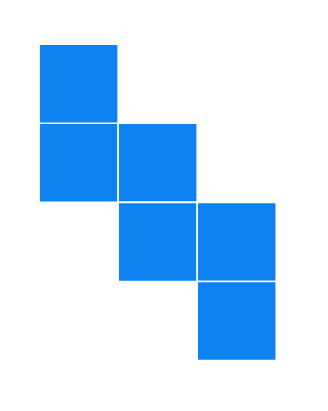
Solution
It can form a cube.
Cannot form a cube: When folded, there will be overlapping faces and a missing face.
(ii). Answer the following questions.
(a) Name the polyhedron which has four vertices, four faces?
Solution
(b) Name the solid object which has no vertex?
Solution
(c) Name the polyhedron which has 12 edges?
Solution
(d) Name the solid object which has one surface?
Solution
(e) How a cube is different from cuboid?
Solution
A cube has all its sides as
(f) Name the two shapes which have the same number of edges, vertices and faces.
Solution
(g) Name the polyhedron which has 5 vertices and 5 faces?
Solution
(iii). Write the names of the objects given below.
(a)
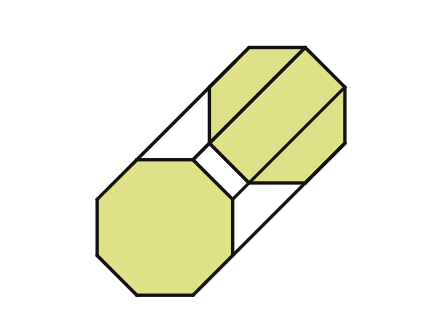
Solution
(b)

Solution
(c)
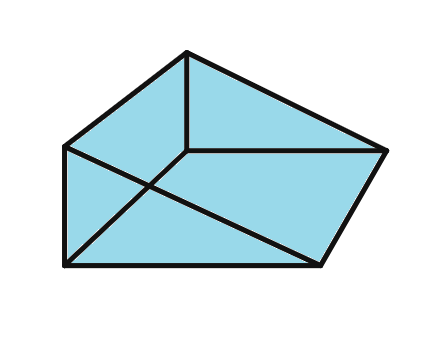
Solution
(d)

Solution
