Surface Area of Cuboid
Say, we have a cuboidal, cubical and a cylindrical box- all having the same height. If these boxes need to be painted, can you deduce which box requires more amount of paint? Logically, we know that the box with the most amount of surface area will be using up more paint? But which box has the highest value of surface area?
To find the total surface area of any object, we need to find the area of each face of that object and add up all the values. Thus,
The surface area of a solid is the sum of the areas of its faces.
Cuboid
A cuboid is a 3D object, having the length, breadth and height as dimensions (the values for atleast two dimensions is unequal) and the opposite faces are identical.
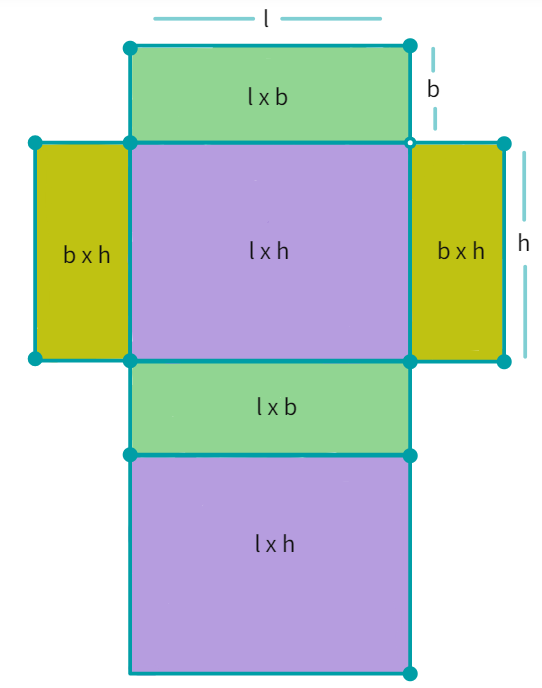
Since, a cuboid has a total of six faces- it has
To find the total surface area:
The Total surface area of a cuboid = h × l + b × l + b × h + l × h + b × h + l × b
= 2(lb + bh + hl)
Total surface area = 2 (h × l + b × h + b × l) = 2(lb + bh + hl)
where h, l and b are the height, length and width of the cuboid respectively.
When we consider, the surface of a room to be painted, how much paint will be needed? We realize that the roof and floor need not be included for this calculation. Like this, there are many cases where only the sides (excluding the top and base) of the solid need to be taken into account. In such cases, we calculate the lateral surface area.
In the case regarding the room, we calculate the lateral surface area of the cuboid.
Lateral surface area of a cuboid = 2(h × l + b × h) (or) 2h (l + b)
Can we say that:
Total surface area of cuboid = lateral surface area + 2 × area of base?
We have a cuboid with length (l), breadth(b) and height (h), where the numerical values for all the dimensions are different.If we interchange the length and the height of the cuboid to obtain a new cuboid, will its lateral surface area change?
The new lateral surface area will be equal to:
Given: length = 15 cm , breadth = 10 cm and height = 20cm, find the value of the surface area of the cuboid.
- Substituting the values, we get: Surface Area =
cm 2 - Substituting the values
- Adding
- We have found the result.
TRY THESE
Find the total surface area of the following cuboids:
Volume is the amount of space occupied by an object. To understand this concept, let’s perform a simple experiment using water displacement.
Activity to Measure Volume of a Solid Object
1. Take a transparent glass jar and place it inside a larger container to collect overflowed water.
2. Fill the jar completely with water up to its brim.
3. Gently drop a solid object (e.g., a stone) into the jar.
The object will sink, and water will spill over into the outer container.
4. Collect the spilled water in a measuring jar.
The amount of water displaced is
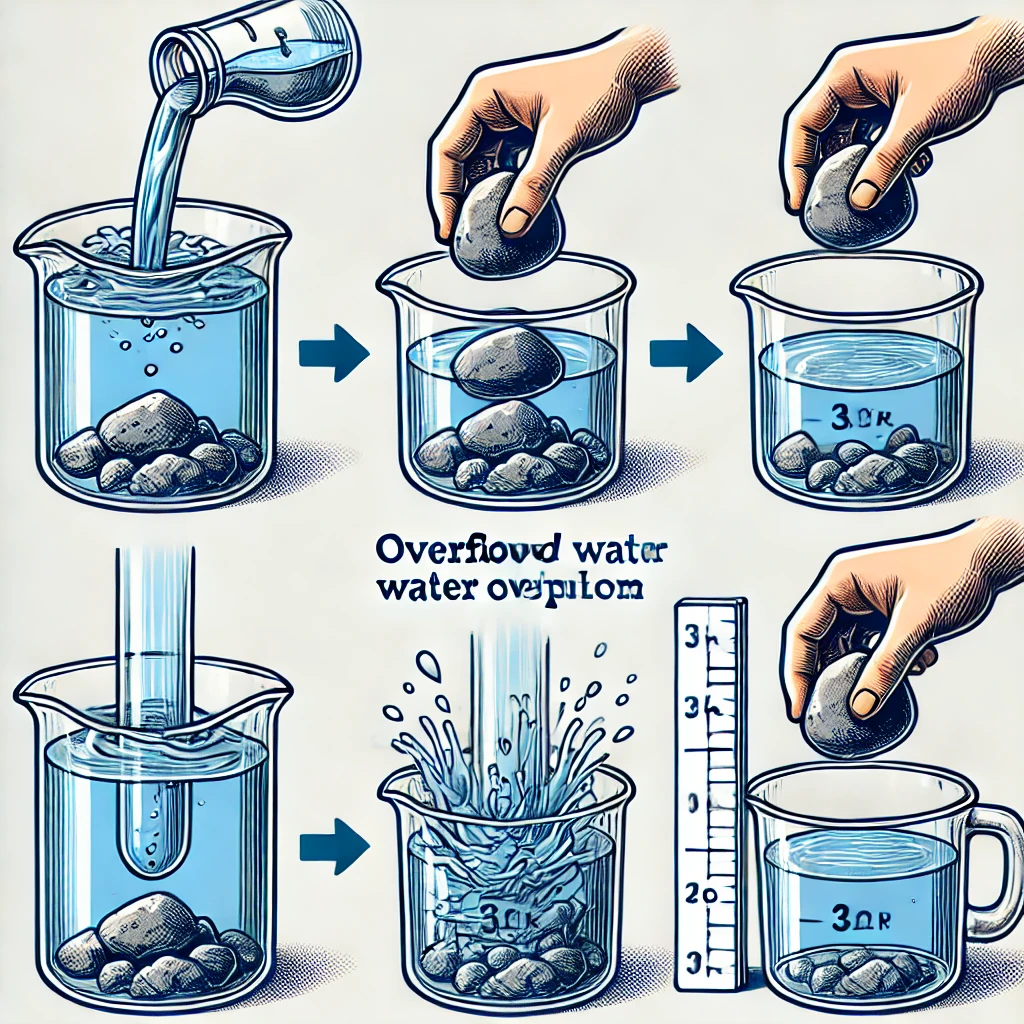
This experiment demonstrates how volume is the space occupied by an object, measured in cubic units (e.g.,
A container's capacity refers to the maximum volume of liquid or substance it can hold. If an object is hollow, its interior can be filled with air, water, or any other substance, taking the shape of the container.
Volume of a Cuboid
A cuboid is a three-dimensional shape with length (l), breadth (b), and height (h). The volume of a cuboid is calculated by determining the space it occupies.
How to Find the Volume of a Cuboid?
1. Imagine stacking multiple rectangles of the same size one over another. The shape formed is a
2. The area of one rectangle is given by: Area =
3. The total space occupied by the cuboid is found by multiplying the area of the rectangle by its height (h): Volume =
4. Thus, the formula for the volume of a cuboid is: V = l × b × h
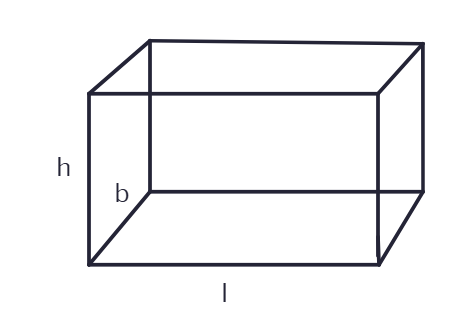
Where:
l = length of the cuboid
b = breadth (width) of the cuboid
h = height of the cuboid
