Volume of Cube, Cuboid and Cylinder
We have spoken about surface area but another very important related quantity when it comes to solids and shapes is Volume. The amount of space occupied by a three dimensional object is called its volume. For example: The space is a room is greater than the space in a cabinet. In other words, the volume of the room is greater than the volume of the cabinet. Similarly, the volume of a pencil box will be greater than the volume of the pen and the eraser kept inside it.
In terms of real life applications, how many bottles of water can we place in a small store room? What is the amount of milk that can be carried by the milkman if he has two containers with a fixed value of dimensions? Such problems can only be solved when we check for the related volumes.
Now, how to measure the volume of any of these objects?
We use square units-

The volume of a solid can be said to be measured by counting the number of unit cubes it contains. Cubic units which we generally use to measure volume is equal to:
1 cubic cm = 1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm = 1
1 cubic m = 1 m × 1 m × 1 m = 1
1 cubic mm = 1 mm × 1 mm × 1 mm = 1 m
Let's start by finding the volume formula for the basic shapes of cube, cuboid and cylinder.
Cuboid
In the below table, consider the sides and assign them the designation of "length" , "breadth" and "height". Now, take the numerical values and find the product of
| S.No | Cuboid | l×b×h |
|---|---|---|
| (i) |  | |
| (ii) |  | |
| (iii) |  |
We observe that the numerical value of the product
Since,
Volume of cuboid = Area of base × height
Volume of cuboid = area of the base × height = l x b x h
Take 36 cubes of equal size (i.e., length of each cube is same). Arrange them to form a cuboid. What do you observe? Since we have used 36 cubes to form these cuboids, volume of each cuboid is 36 cubic units. Also volume of each cuboid is equal to the product of length,
Try These
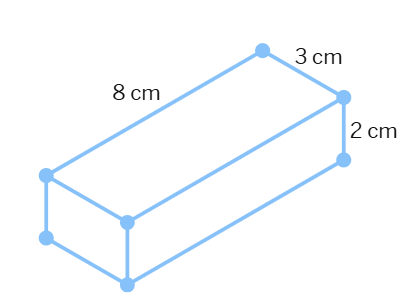
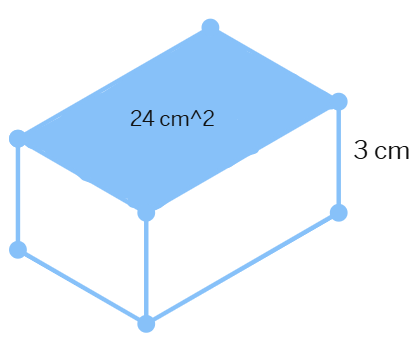
Find the volume of the following cuboids.
Cube
We have already spoken about how, the cube is a special case of a cuboid where l = b = h. By simply putting this condition into the above equation for volume of cuboid:
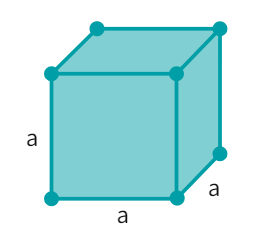
- Let l = b = h = a. Thus, volume of cuboid with all sides equal i.e. a cube:
unit 3 - Thus, volume of cube becomes as shown.
Thus,
Volume of cube = a3
where, a is the cube side length.
TRY THESE
Find the volume of the following cubes: (a) with a side 4 cm (b) with a side 1.5 m
Arrange 64 cubes of equal size in as many ways as you can to form a cuboid. Find the surface area of each arrangement. Can solid shapes of same volume have same surface area?
Cylinder
When it comes to the volume of the cylinder - similar to cuboid, a cylinder has got a top and a base which are congruent and parallel to each other and its lateral surface is perpendicular to the base.

We also know that the volume of a cuboid can be found by finding the product of area of base and its height. Using that same logic to cylinders, we get:
- Volume of a cylinder: (circular base) x (height)
- Thus, if cylinder radius and height are r and h respectively, the volume of a cylinder:
unit 3 - Thus, volume of a cylinder becomes as shown.
Thus,
Volume of cylinder = area of base × height = πr2 x h = πr2h
A company sells biscuits. For packing purpose they are using cuboidal boxes:
(1) Box A = 3 cm × 8 cm × 20 cm
(2) Box B = 4 cm × 12 cm × 10 cm
What size of the box will be economical for the company?
- First, let's calculate the volume of both the boxes.
- Volume(Box A) =
cm 3 cm 3 - We see that both are equal.
- In order to check which box is more economical, we can check the material used for packaging i.e. we need to calculate the
of the boxes. Also - Surface area of a box of length l, breadth b and height h =
- Thus, Surface area for A = Material needed for box A =
cm 2 - Surface area for B = Material needed for box B =
cm 2 - Thus,
is more economical as it will be using lesser amount of material. - Thus, Box B is more economical for the manufacturers.
Find the volume of the following cylinders.
(i) r = 7 cm and h = 10 cm
(ii) base area = 250
