Enhanced Curriculum Support
This is a comprehensive educational resource designed to provide students with the tools and guidance necessary to excel. This support system is structured to cater to various aspects of learning, ensuring that students are well-prepared for academic challenges and practical applications of mathematical concepts. Some are the key benefits are mentioned below:
1.Comprehensive Learning: This holistic approach helps students gain a thorough understanding of the subject. Practical Application: The resources encourage students to apply mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios, enhancing their practical understanding and problem-solving skills.
2.Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Value-Based and HOTS questions promote critical thinking and reasoning abilities. These skills are crucial for students to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions.
3.Exam Preparedness: Sample Question Papers and NCERT Exemplar Solutions provide ample practice for exams. They help students familiarize themselves with the exam format and types of questions, reducing exam anxiety.
4.Ethical and Moral Development: Value-Based Questions integrate ethical and moral lessons into the learning process, helping in the overall development of students' character and social responsibility. By incorporating these diverse elements, Enhanced Curriculum Support aims to provide a robust and well-rounded knowledge, preparing students for both academic success and real-world challenges.
Sample Question Papers
Sec A
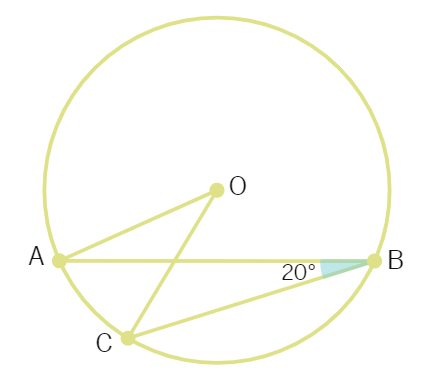
1. In the figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠ABC = 20°, then ∠AOC is equal to :
(a) 60° (b) 10° (c) 40° (d) 20°
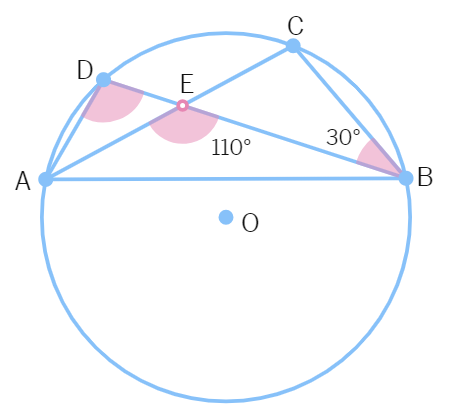
2. In the given figure, O is the centre of a circle and chords AC and BD intersect at E. If AEB = 110° and CBE = 30°, then ADB = ?
(a) 80° (b) 60° (c) 90° (d) 70°
3. In the given figure, a circle is centred at O. The value of x is :
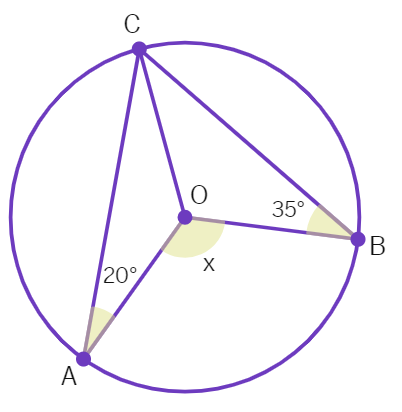
(a) 110° (b) 55° (c) 125° (d) 70°
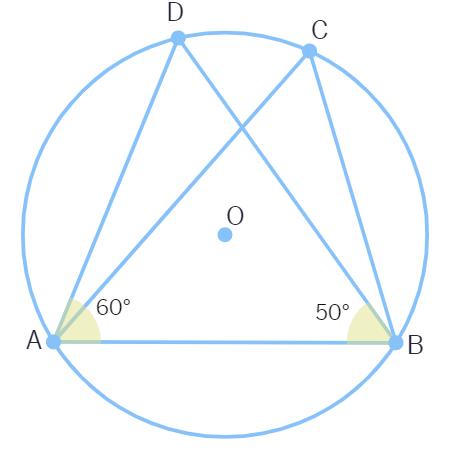
4. In the figure, if ∠DAB = 60° , ∠ABD = 50° then ∠ACB is equal to :
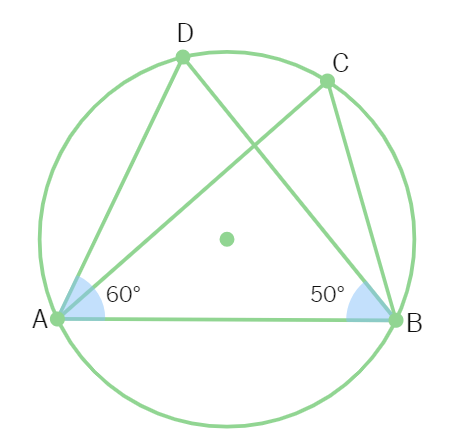
(a) 80° (b) 60° (c) 50° (d) 70°
5. In the given, AB is side of regular five sided polygon and AC is a side of a regular six sided polygon inscribed in the circle with centre O. AO and CB intersect at P, then ∠APB is equal to:
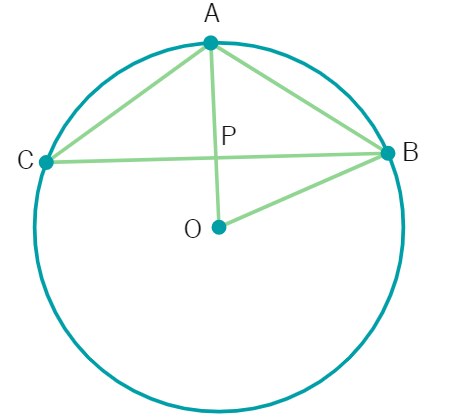
(a) 90° (b) 72° (c) 86° (d) 96°
6. AOB is the diameter of the circle. If ∠AOE = 150°, then the measure of ∠CBE is:
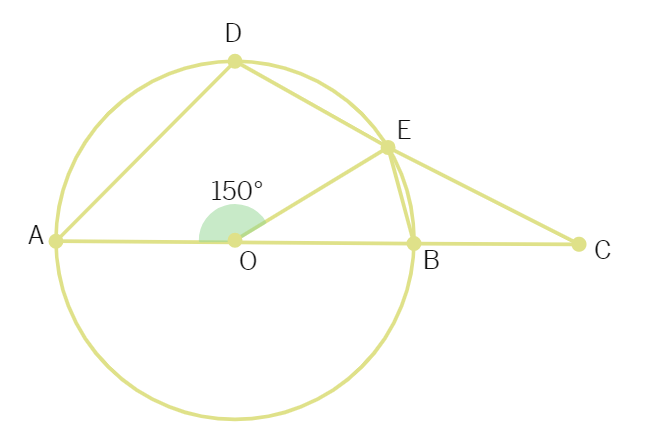
(a) 115° (b) 125° (c) 120° (d) 105°
7. In Fig. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If ∠BAC = 50° and ∠DBC=60° then find ∠BCD:
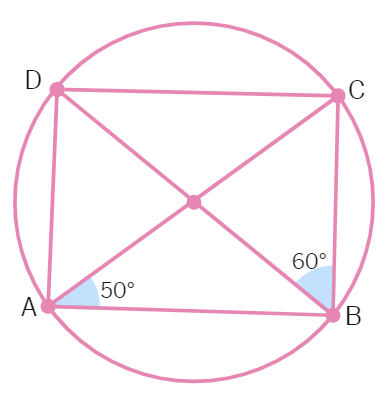
(a) 50° (b) 60° (c) 70° (d) 55°
8. In a figure, O is the centre of the circle with AB as diameter. If ∠AOC = 40°, the value of x is equal to:
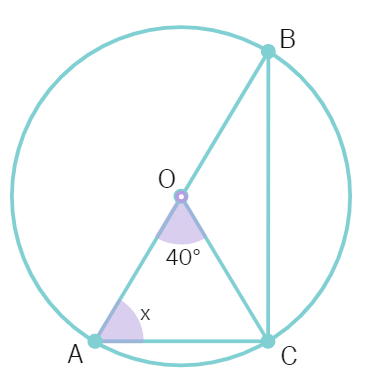
(a) 80° (b) 50° (c) 70° (d) 60°
Sec B
1. Find an angle marked as x in given figure where O is the centre of the circle:
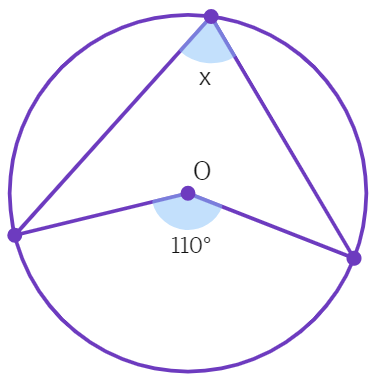
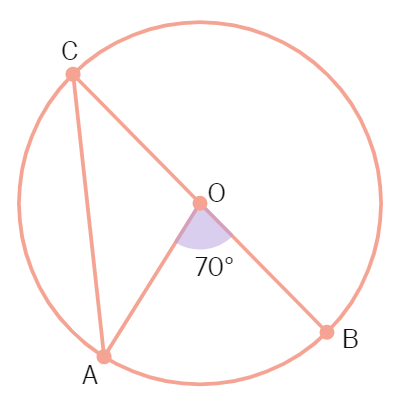
2. In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle and AOB = 70°. Calculate the values of (i) OCA, (ii) OAC.
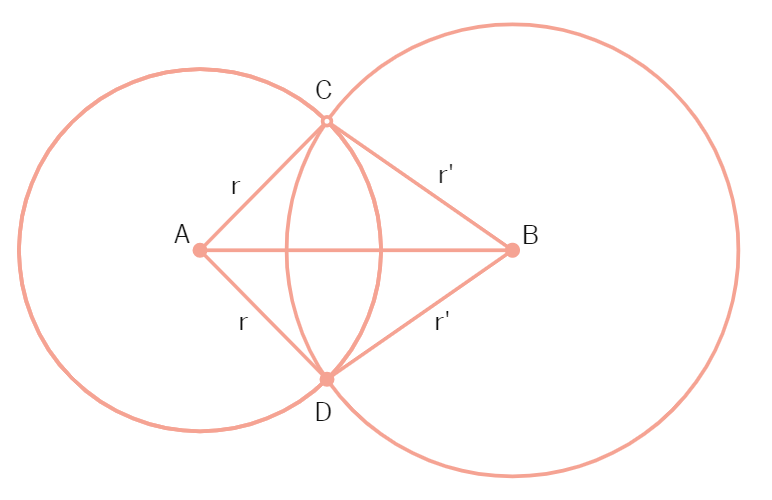
(OR)
Prove that the line of centres of two intersecting circles subtends equal angles at the two points of intersection.
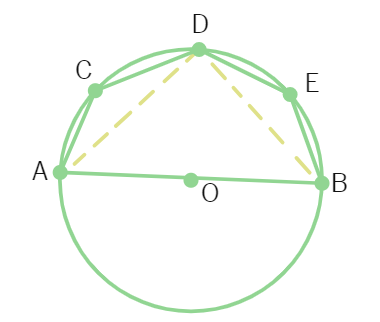
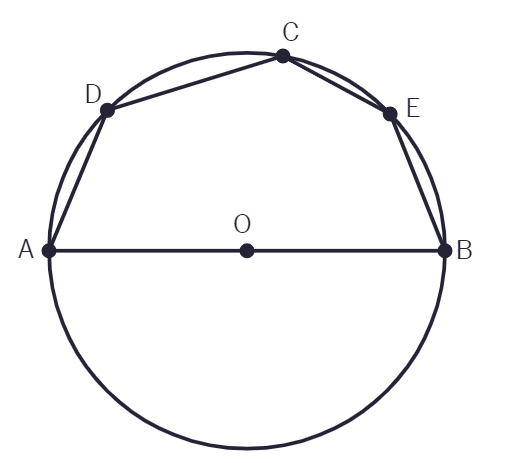
3. In given figure, AOB is a diameter of the circle and C, D, E are any three points on the semi-circle. Find the value of ∠ ACD + ∠ BED.
4. In the given figure, two circles intersect at two points A and B. AD and AC are diameters to the two circles. Prove that B lies on the line segment DC.
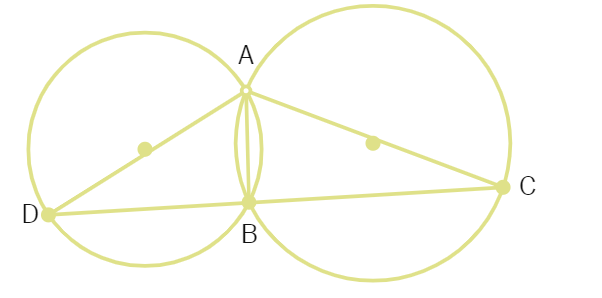
(OR)
If O is the centre of the circle, find the value of x in given figure:
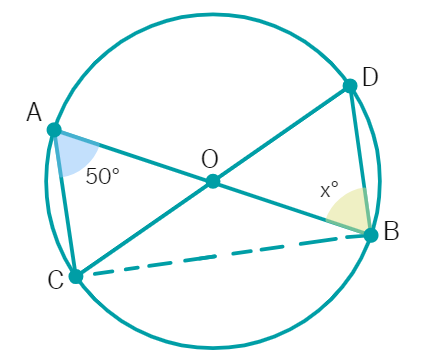
Sec C
1. Rohan draws a circle of radius 10 cm with the help of a compass and scale. He also draws two chords, AB and CD in such a way that the perpendicular distance from the center to AB and CD are 6 cm and 8 cm respectively. Now, he has some doubts that are given below.
(i) Show that the perpendicular drawn from the Centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
(ii) What is the length of CD?
(iii) What is the length of AB?
OR
How many circles can be drawn from given three noncollinear points?
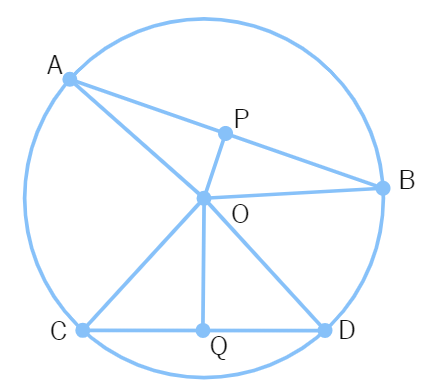
2. Sanjay and his mother visited in a mall. He observes that three shops are situated at P, Q, R as shown in the figure from where they have to purchase things according to their need. Distance between shop P and Q is 8 m and between shop P and R is 6 m. Considering O as the center of the circles.
(i) Find the Measure of QPR.
(ii) Find the radius of the circle.
(iii) Find the Measure of QSR.
OR
Find the area of Δ PQR.
3. Two new roads, Road E and Road F were constructed between society 4 and 1 and society 1 and 2.
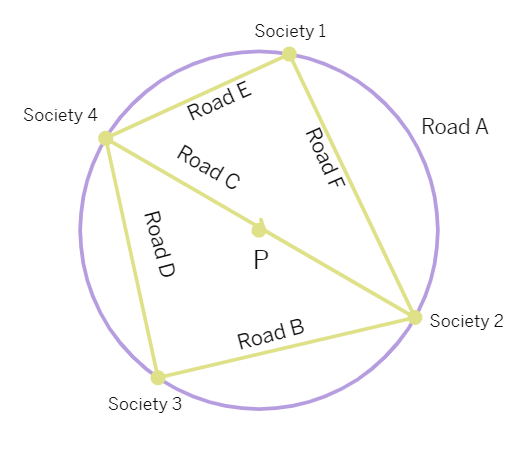
(i) What would be the measure of the sum of angles formed by the straight roads at Society 1 and society 3?
(a) 60° (b) 90° (c) 180° (d) 360°
(ii) Krish says, The distance to go from society 4 to society 2 using Road D will be longer that the distance using Road E. Is Krish correct? Justify your answer with examples.
(iii) Road G, perpendicular to Road F was constructed to connect the park and Road F. Which of the following is true for Road G and Road F?
(a) Road G and road F are of same length.
(b) Road F divides Road G into two equal parts.
(c) Road G divides Road F into two equal parts.
(d) The length of road G is one-fourth of the length of Road F.
(iv) Priya said, Minor arc corresponding to Road B is congruent to minor arc corresponding to Road D. Do you agree with Priya? Give reason to supportyour answer.
Value Based Questions
Problem 1
A neighborhood is planning to install a circular fountain in a park as a way of beautifying the area and creating a peaceful atmosphere. The circumference of the fountain is 31.4 meters. Calculate the radius of the fountain and discuss how having community spaces like parks contributes to a sense of peace and relaxation.
The question promotes the values of community beautification, creating spaces for relaxation, and fostering a peaceful environment for all.
Problem 2
A city is organizing a charity run event around a circular lake. The diameter of the lake is 4 kilometers. If participants are to complete one full round of the lake, what is the total distance they will cover? How does this event support community bonding and physical fitness?
This question emphasizes the importance of community activities and promotes health and fitness, as well as the social value of organizing charity events.
HOTS
Q1
Two circles intersect at points P and Q. A line passing through P intersects the circles again at points A and B. Prove that AP = BP using geometric properties of circles.
Q2
In a circle, a diameter AB is drawn, and a point P is taken on the circle such that it is not on the diameter. Prove that the angle APB is a right angle. How does this property extend to all points on the circumference of a circle? Provide a logical explanation for this observation.
Q3
A circle is inscribed inside a square. The radius of the circle is r, and the side length of the square is 2r. A smaller circle is drawn tangent to one side of the square and externally tangent to the inscribed circle. Find the radius of the smaller circle in terms of r and justify your solution.
Q4
A sector of a circle with a radius of 10 cm subtends an angle of 90° at the center. Calculate the area of the sector and the length of the arc. If the sector is folded to form a cone, determine the height of the cone. Explain how the relationship between circles and cones helps in solving this.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Choose the correct option
Questions
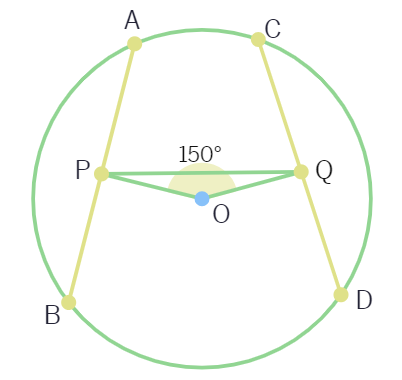
In the below figure, AB and CD are two equal chords of a circle with centre O. OP and OQ are perpendiculars on chords AB and CD, respectively. If ∠POQ = 150º, then ∠APQ is equal to:
(A) 30º (B) 75º
(C) 15º (D) 60º
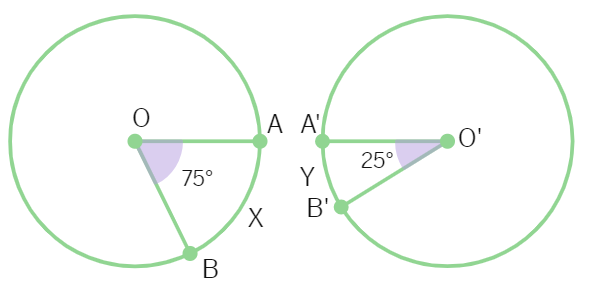
In the given two figures, two congruent circles have centres O and O′. Arc AXB subtends an angle of 75º at the centre O and arc A′ Y B′ subtends an angle of 25º at the centre O′. Then the ratio of arcs A X B and A′ Y B′ is:
(A) 2 : 1 (B) 1 : 2 (C) 3 : 1 (D) 1 : 3
AD is a diameter of a circle and AB is a chord. If AD = 34 cm, AB = 30 cm, the distance of AB from the centre of the circle is:
(A) 17 cm (B) 15 cm (C) 4 cm (D) 8 cm
If AB = 12 cm, BC = 16 cm and AB is perpendicular to BC, then the radius of the circle passing through the points A, B and C is :
(A) 6 cm (B) 8 cm
(C) 10 cm (D) 12 cm
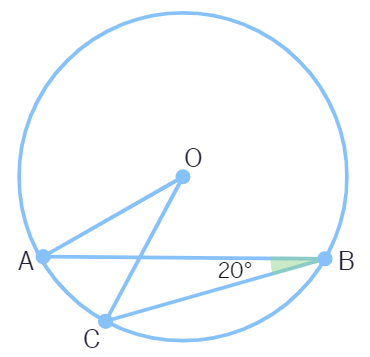
In the below figure, if ∠ABC = 20º, then ∠AOC is equal to:
(A) 20º (B) 40º (C) 60º (D) 10º
In the figure, if ∠OAB = 40º, then ∠ACB is equal to :
(A) 50º (B) 40º (C) 60º (D) 70°
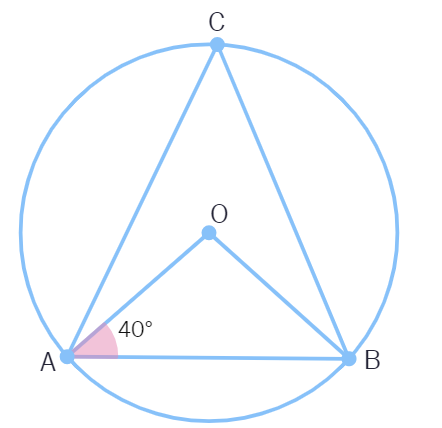
In the below figure, if ∠DAB = 60º, ∠ABD = 50º, then ∠ACB is equal to:
(A) 60º (B) 50º (C) 70º (D) 80º
In the below figure, BC is a diameter of the circle and ∠BAO = 60º. Then ∠ADC is equal to :
(A) 30º (B) 45º
(C) 60º (D) 120º
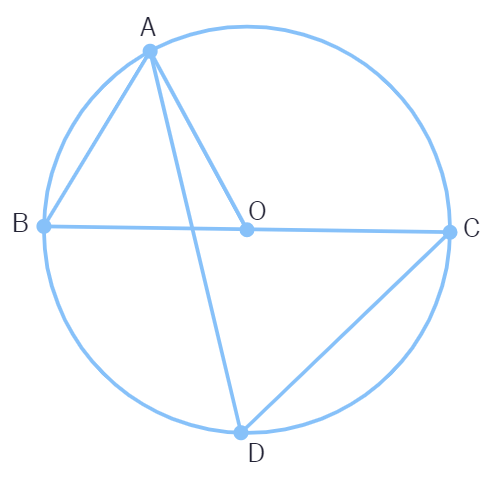
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that AB is a diameter of the circle circumscribing it and ∠ADC = 140º, then ∠BAC is equal to:
(A) 80º (B) 50º
(C) 40º (D) 30º
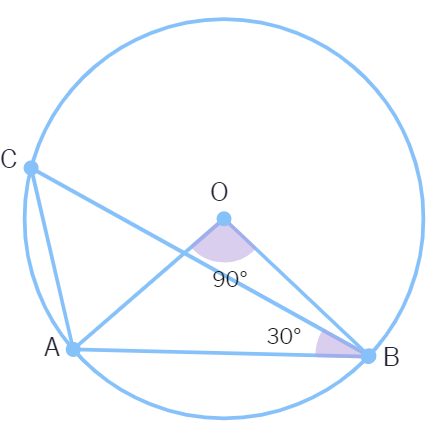
In below figure, ∠AOB = 90º and ∠ABC = 30º, then ∠CAO is equal to:
(A) 30º (B) 45º (C) 90º (D) 60º
Write True or False and justify your answer.
Questions
1. Two chords AB and CD of a circle are each at distances 4 cm from the centre. Then AB = CD.
2. Two chords AB and AC of a circle with centre O are on the opposite sides of OA. Then ∠OAB = ∠OAC.
3. Two congruent circles with centres O and O′ intersect at two points A and B. Then ∠AOB = ∠AO′B.
4. Through three collinear points a circle can be drawn.
5. A circle of radius 3 cm can be drawn through two points A, B such that AB = 6 cm.
6.If AOB is a diameter of a circle and C is a point on the circle, then
7. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that ∠A = 90°, ∠B = 70°, ∠C = 95° and ∠D = 105°.
8. If A, B, C, D are four points such that ∠BAC = 30° and ∠BDC = 60°, then D is the centre of the circle through A, B and C.
9. If A, B, C and D are four points such that ∠BAC = 45° and ∠BDC = 45°, then A, B, C, D are concyclic.
10. In the given figure, if AOB is a diameter and ∠ADC = 120°, then ∠CAB = 30°.
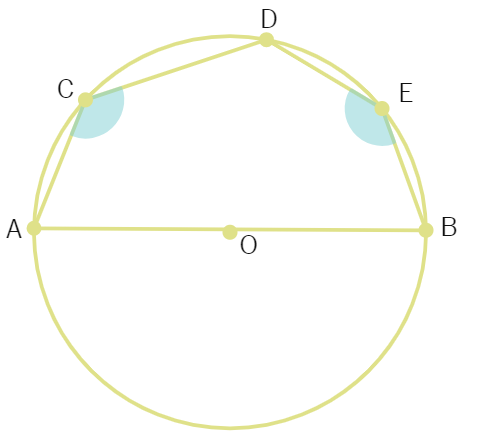
11. The angles subtended by a chord at any two points of a circle are equal.
12. Two chords of a circle of lengths 10 cm and 8 cm are at the distances 8.0 cm and 3.5 cm, respectively from the centre.
Answer the below the questions
Questions
In the figure, AOC is a diameter of the circle and arc AXB =
If the perpendicular bisector of a chord AB of a circle PXAQBY intersects the circle at P and Q, prove that arc PXA ≅ Arc PYB.
AB and AC are two equal chords of a circle. Prove that the bisector of the angle BAC passes through the centre of the circle.
ABCD is such a quadrilateral that A is the centre of the circle passing through B, C and D. Prove that: ∠CBD + ∠CDB =
O is the circumcentre of the triangle ABC and D is the mid-point of the base BC. Prove that ∠BOD = ∠A.
On a common hypotenuse AB, two right triangles ACB and ADB are situated on opposite sides. Prove that ∠BAC = ∠BDC.
Two chords AB and AC of a circle subtends angles equal to 90º and 150º, respectively at the centre. Find ∠BAC, if AB and AC lie on the opposite sides of the centre.
If BM and CN are the perpendiculars drawn on the sides AC and AB of the triangle ABC, prove that the points B, C, M and N are concyclic.
If a line is drawn parallel to the base of an isosceles triangle to intersect its equal sides, prove that the quadrilateral so formed is cyclic.
Two circles with centres O and O′ intersect at two points A and B. A line PQ is drawn parallel to OO′ through A(or B) intersecting the circles at P and Q. Prove that PQ = 2 OO′.
In the figure, AOB is a diameter of the circle and C, D, E are any three points on the semi-circle. Find the value of ∠ACD + ∠BED.
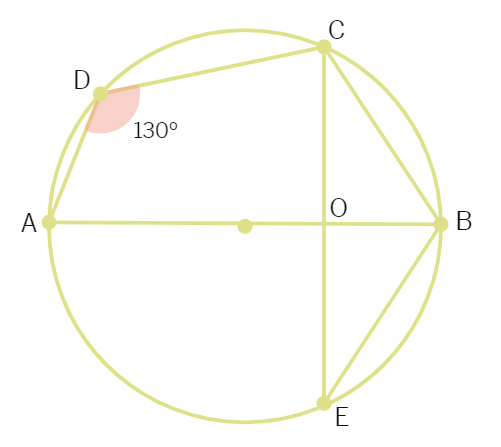
In the below figure, ∠ADC = 130° and chord BC = chord BE. Find ∠CBE.
Prove that among all the chords of a circle passing through a given point inside the circle that one is smallest which is perpendicular to the diameter passing through the point.
Case Based Questions
Q1
A clock is designed with a circular dial. The radius of the dial is 15 cm. The hour and minute hands move around the circumference of the dial. The clockmaker is interested in designing different aesthetic elements for the clock.
Calculate the area of the clock dial.
If the minute hand is 12 cm long, calculate the distance covered by the tip of the minute hand in 60 minutes.
The clockmaker wants to add a border around the dial. If the width of the border is 2 cm, what will be the total area covered by the clock dial and its border?
Discuss the importance of design and functionality in creating objects like clocks.
How can the design of such everyday objects influence their appeal and usefulness?
Q2
A designer is working on a new bicycle wheel with a circular rim. The radius of the wheel is 35 cm. The designer plans to add spokes inside the wheel, joining the center to the rim. If each spoke divides the wheel into equal sectors, the designer adds 7 spokes.
Calculate the length of each spoke.
Determine the angle subtended by two consecutive spokes at the center of the wheel.
If the designer wishes to increase the number of spokes to 14, what will be the new angle between two consecutive spokes?
Discuss how increasing the number of spokes improves the wheel's stability.
How does innovative design impact the efficiency and durability of machines?
