Hard Level Worksheet
Part A: Subjective Questions - Very Short Answer (1 Mark Each)
Note: Answer with complete reasoning and analysis of both symmetry types.
In this hard level, we'll tackle point symmetry, combined symmetries, and advanced applications.
Let's master the most challenging symmetry concepts!
1. What is point symmetry?
Point symmetry is when every point has a
Perfect! Same as rotational symmetry of order 2.
2. Define rotational order.
Rotational order is the
Excellent! Counts identical positions including original.
3. Write one letter with rotational symmetry but no line symmetry.
Letter:
Correct! S, N, Z have order 2 but no line symmetry.
4. Write one shape with both line and rotational symmetry.
Shape:
Perfect! Regular polygons have both types.
5. What is the order of rotational symmetry for a circle?
Order:
Excellent! Circle looks same at any rotation angle.
6. What is the order of rotational symmetry for an equilateral triangle?
Order:
Rotation angle: 360 ÷ 3 =
Perfect! Rotates every 120 degrees.
7. Which English letter has one line of symmetry and order 2 rotational symmetry?
This is
If order 2, shape looks same after
But shapes with order 2 typically have
Correct! This combination is rare/impossible in standard letters.
8. Name any shape which has diagonal symmetry.
Shape:
Square has
Perfect! Square's diagonals are symmetry lines.
9. Define centre of rotation.
Centre of rotation is the
Excellent! The point that doesn't move during rotation.
10. What is the difference between rotational and line symmetry?
Line symmetry: Uses
Rotational symmetry: Uses
Perfect! Two fundamentally different transformations.
Drag each shape to its symmetry category:
Part A: Section B – Short Answer Questions (2 Marks Each)
Problem 1: For Letter A, determine: Number of lines of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry.

Lines of symmetry:
Order of rotation:
Perfect! Letter A has line symmetry only.
Problem 2: For Letter H, determine: Number of lines of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry.
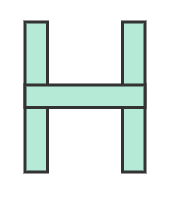
Lines of symmetry:
Order of rotation:
Excellent! Letter H has both types.
Problem 3: For Letter N, determine: Number of lines of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry.
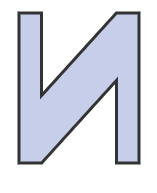
Lines of symmetry:
Order of rotation:
Great! Letter N has only rotational symmetry.
Problem 4: Which shapes have BOTH line symmetry AND rotational symmetry of order 4 or more?
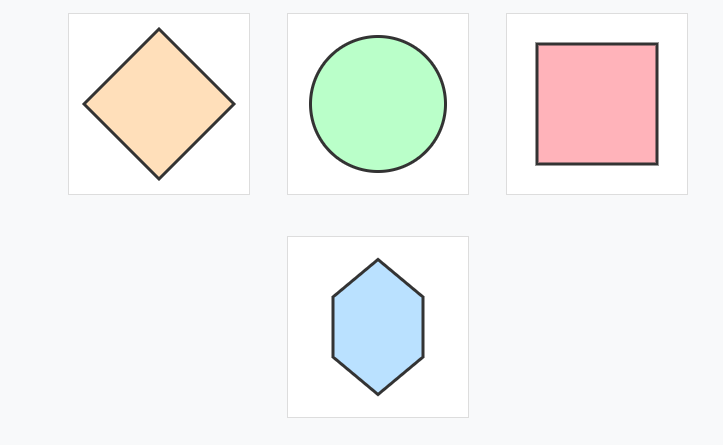
Rhombus: Lines =
Circle: Lines =
Square: Lines =
Perfect! Circle and Square qualify (order ≥ 4).
Problem 5: Write differences between line and rotational symmetry in tabular form.
Create comparison table:
Line Symmetry:
Transformation:
Across:
Creates:
Rotational Symmetry:
Transformation:
Around:
Measured by:
Perfect! Clear distinction between the two types.
Part A: Section C – Long Answer Questions (4 Marks Each)
1. For shapes A, H, N, draw and show both types of symmetry.
Letter A:
Lines of symmetry:
Order of rotation:
Letter H:
Lines of symmetry:
Order of rotation:
Letter N:
Lines of symmetry:
Order of rotation:
Perfect! Three letters with different symmetry patterns.
2. Draw diagrams to show symmetry in square, circle, and equilateral triangle.
Draw on your answer sheet:
Square:
Lines =
Circle:
Lines =
Equilateral Triangle:
Lines =
Excellent! All three are highly symmetrical shapes.
3. Explain how rotational symmetry appears in designs (e.g., rangoli, wheels).
Rangoli patterns:
Use
Typically order
Creates
Wheel designs:
Spokes arranged with
Order depends on number of
Ensures
Perfect! Rotational symmetry is functional and beautiful.
4. Verify the order of rotational symmetry for regular polygons.
General rule:
Regular n-sided polygon has order
Rotation angle = 360 ÷
Examples:
Triangle (3 sides): Order =
Square (4 sides): Order =
Pentagon (5 sides): Order =
Hexagon (6 sides): Order =
Excellent! Clear pattern for all regular polygons.
5. Draw and identify real-life examples of symmetry (flowers, butterflies, logos).
Draw on your answer sheet:
Flowers:
Type:
Order: Depends on number of
Butterflies:
Type:
Lines:
Logos:
Often have
Creates
Perfect! Symmetry is everywhere in nature and design.
Part B: Objective Questions - Test Your Knowledge!
Answer these multiple choice questions:
6. A square has:
(a) 4 lines of symmetry (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 6
Correct! Square has 4 lines: 2 diagonals + vertical + horizontal.
7. A parallelogram has:
(a) 2 lines (b) 1 line (c) None (d) Infinite lines
Perfect! Parallelogram has NO line symmetry but has rotational order 2.
8. The order of rotation of a regular hexagon is:
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6
Excellent! Regular hexagon has 6 sides, so order 6.
9. A figure looks same after half turn (180°). Its rotational order is:
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Correct! Half turn (180°) means order 2.
10. Rotational symmetry means:
(a) Turning around a point (b) Reflecting over line (c) Sliding (d) Folding
Perfect! Rotational symmetry is rotation around a center point.
🏆 Outstanding Achievement! You've Mastered Advanced Symmetry!
Here's what you've conquered at the hard level:
Point Symmetry:
Definition:
- Every point has matching point opposite center
- Equal distance from center
- Equivalent to rotational order 2
Examples:
- Letter S, N, Z
- Parallelogram
- Rectangle
Key property:
- Looks same after 180° rotation
- Special case of rotational symmetry
Complete Symmetry Analysis Framework:
For any shape, determine:
- Number of lines of symmetry
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Whether has both, one, or neither
- Practical applications
Example - Square:
- Lines: 4 (2 diagonals + vertical + horizontal)
- Order: 4 (rotates every 90°)
- Has both types (highly symmetrical)
Combined Symmetry Patterns:
Shape Lines Order Type Square 4 4 Both Rectangle 2 2 Both Rhombus 2 2 Both Equilateral Triangle 3 3 Both Circle ∞ ∞ Both (maximum) Parallelogram 0 2 Rotational only Letter S, N, Z 0 2 Rotational only Letter A, M 1 1 Line only Scalene Triangle 0 1 Neither Regular Polygon Symmetry Pattern:
Universal rule:
- n-sided regular polygon
- Has n lines of symmetry
- Has rotational order n
- Rotation angle = 360°/n
Examples:
- Triangle: 3 lines, order 3, 120°
- Square: 4 lines, order 4, 90°
- Pentagon: 5 lines, order 5, 72°
- Hexagon: 6 lines, order 6, 60°
- Octagon: 8 lines, order 8, 45°
Letter Symmetry Classification:
No symmetry: F, G, J, L, P, Q, R
Line only (order 1):
- Vertical: A, M, T, U, V, W, Y
- Horizontal: B, C, D, E, K
Both line and rotational (order 2):
- H, I, O, X (2 lines each)
Rotational only (order 2):
- N, S, Z (0 lines)
Advanced Rotation Calculations:
Finding rotation angle:
- Angle = 360° ÷ order
- Example: Order 5 → 360°/5 = 72°
Finding order from angle:
- Order = 360° ÷ angle
- Example: 120° → 360°/120° = 3
Verifying order:
- Rotate shape at calculated angle
- Check if it looks identical
- Count positions until 360°
Center of Rotation:
Definition:
- Fixed point during rotation
- Shape rotates around this point
- Doesn't move itself
Location:
- Usually geometric center of shape
- For regular polygons: center
- For letters: varies
Importance:
- Defines axis of rotation
- Determines symmetry pattern
- Essential for analysis
Symmetry in Real-World Design:
Architecture:
- Buildings often symmetrical
- Facades use line symmetry
- Floor plans use rotational patterns
Nature:
- Flowers: rotational (petal count)
- Butterflies: bilateral (1 line)
- Starfish: rotational (usually order 5)
- Snowflakes: rotational order 6
Art and Culture:
- Rangoli: high rotational order
- Mandalas: circular symmetry
- Logos: both types for balance
- Islamic art: complex rotational patterns
Engineering:
- Wheels: rotational symmetry
- Gears: practical rotational order
- Propellers: aerodynamic symmetry
Problem-Solving Strategy:
For line symmetry:
- Try folding shape mentally
- Check if halves match
- Count all possible fold lines
For rotational symmetry:
- Mark a reference point
- Rotate shape mentally
- Check identical positions
- Count before returning to start
For combined analysis:
- Find all lines first
- Then check rotational order
- Look for patterns
- Verify calculations
Advanced Concepts:
Relationship between symmetries:
- High line count → high rotational order (usually)
- But not always (parallelogram: 0 lines, order 2)
- Circle: infinite of both (perfect symmetry)
Symmetry breaking:
- Small change breaks symmetry
- Important in physics and chemistry
- Explains many natural phenomena
Symmetry groups:
- Mathematical classification
- Dihedral groups for regular polygons
- Cyclic groups for rotational only
Critical Thinking Applications:
- Identify symmetry in complex patterns
- Design symmetrical objects
- Analyze logo effectiveness
- Understand crystal structures
- Appreciate artistic patterns
- Solve geometric puzzles
Common Advanced Mistakes:
- Confusing order with number of lines
- Forgetting shapes can have rotational but no line
- Miscounting positions during rotation
- Not including original position in order count
- Assuming all shapes with lines have rotation
- Wrong calculation of rotation angle
Mastery Checklist: ✓ Identify both symmetry types in any shape ✓ Calculate rotational order and angle ✓ Recognize patterns in regular polygons ✓ Distinguish between symmetry types ✓ Analyze letter symmetries ✓ Apply to real-world situations ✓ Solve complex symmetry problems ✓ Design symmetrical patterns
Mastering symmetry reveals the hidden order in mathematics, nature, and art!
Remember: Symmetry is about transformation - reflection OR rotation!
Key to success: Practice identifying both types, calculate systematically, and appreciate beauty!
