Moderate Level Worksheet
Part A: Subjective Questions - Very Short Answer (1 Mark Each)
Note: Answer with proper reasoning and clear diagrams showing rotations.
In this moderate level, we'll explore rotational symmetry, order of rotation, and mirror images.
Let's deepen our understanding of symmetry!
1. Define reflection symmetry.
Reflection symmetry is when a shape has a
Perfect! Same as line or mirror symmetry.
2. What is rotational symmetry?
Rotational symmetry is when a shape looks the
Excellent! Shape fits onto itself during rotation.
3. What is the order of rotational symmetry?
Order of rotational symmetry is the
Correct! Number of identical positions in one complete turn.
4. What is a mirror image?
A mirror image is the
Perfect! Like seeing your reflection in a mirror.
5. Write two shapes having no line of symmetry.
Shape 1:
Shape 2:
Great! These shapes have no reflection symmetry.
6. Which shape has infinite lines of symmetry?
Shape:
Perfect! Every diameter of a circle is a line of symmetry.
7. What is the order of rotational symmetry for a square?
Order:
Looks same at:
Excellent! Square has rotational order 4.
8. Name a shape that has rotational symmetry but no line symmetry.
Example:
Correct! Some shapes rotate but don't reflect.
9. Write two examples of letters that have one vertical line of symmetry.
Letter 1:
Letter 2:
Perfect! These letters fold vertically.
10. Draw a shape with exactly one line of symmetry.
Example:
Or:
Great! These shapes have exactly one line of symmetry.
Drag each shape to its rotational symmetry order:
Part A: Section B – Short Answer Questions (2 Marks Each)
Problem 1: Does a square have rotational symmetry? If yes, state the order.
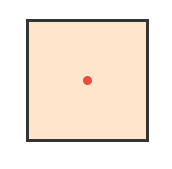
Answer:
Order:
Rotates into itself at:
Perfect! Square has rotational order 4.
Problem 2: Does an equilateral triangle have rotational symmetry? If yes, state the order.
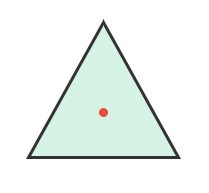
Answer:
Order:
Rotates into itself at:
Excellent! Equilateral triangle has order 3.
Problem 3: Does a parallelogram have rotational symmetry? If yes, state the order.
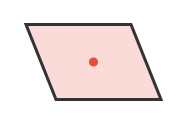
Answer:
Order:
Rotates into itself at:
Great! Parallelogram has rotational order 2, but NO line symmetry.
Problem 4: What is the order of rotational symmetry for a rectangle?

Order:
Angles:
Perfect! Rectangle looks same after half turn.
Problem 5: What is the order of rotational symmetry for a regular hexagon?
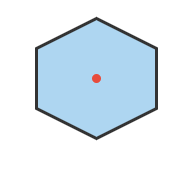
Order:
Angles:
Excellent! Regular hexagon has order 6.
Part A: Section C – Long Answer Questions (4 Marks Each)
1. Explain with diagrams how rotational symmetry works in square and hexagon.
Square:
Order of rotation:
Rotates every: 360 ÷ 4 =
Positions: at
Hexagon:
Order of rotation:
Rotates every: 360 ÷ 6 =
Positions: at
Perfect! Both shapes have rotational symmetry.
2. Find the order of rotational symmetry for: Square, Rectangle, Regular hexagon.
Square: Order =
Rectangle: Order =
Regular hexagon: Order =
Excellent! Pattern: regular n-gon has order n.
3. Draw and explain the mirror image of letters A, H, and N.
Draw on your answer sheet:
Letter A:
Has
Mirror image looks
Letter H:
Has
Mirror image looks
Letter N:
Has
Has rotational symmetry of order
Great! Different letters have different symmetries.
4. Compare line and rotational symmetry using diagrams.
Draw on your answer sheet:
Line symmetry:
Uses
Creates
Rotational symmetry:
Uses
Shape looks
Some shapes have:
Perfect! Two different types of symmetry.
5. Explain how symmetry appears in nature and art.
Nature examples:
Art examples:
Excellent! Symmetry is everywhere in nature and design.
Part B: Objective Questions - Test Your Knowledge!
Answer these multiple choice questions:
6. A circle has rotational symmetry of order:
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) Infinite (d) None
Correct! Circle looks same at any angle of rotation.
7. Mirror symmetry is also known as:
(a) Reflection symmetry (b) Rotational symmetry (c) Parallel symmetry (d) None
Perfect! Mirror symmetry = Reflection symmetry = Line symmetry.
8. A shape with both line and rotational symmetry is:
(a) Square (b) Circle (c) Rhombus (d) All
Excellent! Square, circle, and rhombus all have both types.
9. Letter N has how many lines of symmetry?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 4
Correct! Letter N has no line symmetry but has rotational order 2.
10. Which shape shows order 3 rotational symmetry?
(a) Equilateral triangle (b) Square (c) Rectangle (d) Circle
Perfect! Equilateral triangle rotates every 120° (order 3).
🌟 Excellent Progress! You've Mastered Rotational Symmetry!
Here's what you've learned:
Rotational Symmetry Definition:
What is it?
- Shape looks identical after rotation
- Rotation less than 360°
- Fits onto itself at certain angles
Center of rotation:
- Point around which shape rotates
- Usually at center of shape
- Stays fixed during rotation
Order of Rotational Symmetry:
Definition:
- Number of identical positions in 360° rotation
- Includes the original position
- Formula: Angle of rotation = 360° ÷ order
Examples:
- Order 2 → rotates every 180°
- Order 3 → rotates every 120°
- Order 4 → rotates every 90°
- Order 6 → rotates every 60°
Rotational Orders for Common Shapes:
Square: Order 4
- Looks same at: 90°, 180°, 270°, 360°
Rectangle: Order 2
- Looks same at: 180°, 360°
Equilateral Triangle: Order 3
- Looks same at: 120°, 240°, 360°
Regular Pentagon: Order 5
- Looks same at: 72°, 144°, 216°, 288°, 360°
Regular Hexagon: Order 6
- Looks same at: 60°, 120°, 180°, 240°, 300°, 360°
Circle: Order Infinite
- Looks same at any angle
Parallelogram: Order 2
- But NO line symmetry!
Shapes with Rotational but NO Line Symmetry:
- Parallelogram (order 2)
- Letter S (order 2)
- Letter N (order 2)
- Letter Z (order 2)
- These rotate but don't reflect!
Comparing Line and Rotational Symmetry:
Shape Lines Order Square 4 4 Rectangle 2 2 Equilateral Triangle 3 3 Circle ∞ ∞ Parallelogram 0 2 Scalene Triangle 0 1 Pattern Recognition:
Regular polygons:
- n-sided regular polygon
- Has n lines of symmetry
- Has rotational order n
Special cases:
- Some shapes have rotation but no reflection
- Some shapes have reflection but less rotation
- Circle has infinite of both
Mirror Images:
Creating mirror image:
- Reflect each point across line
- Distance from line stays same
- Orientation reverses
Examples:
- Letter A → remains A (symmetrical)
- Letter R → becomes backwards (not symmetrical)
- Letter H → remains H (symmetrical both ways)
Symmetry in Letters:
Rotational only (no lines):
- S, N, Z (order 2)
Line only (order 1):
- A, M, T, U, V, W, Y (vertical)
- B, C, D, E (horizontal)
Both line and rotational:
- H, I, O, X (order 2, 2 lines each)
Testing for Rotational Symmetry:
- Mark the shape's position
- Rotate around center point
- Check if it looks identical
- Count how many times before 360°
- That's the order!
Applications:
- Wheel designs (rotational order high)
- Flowers (natural rotational symmetry)
- Logos (often symmetrical for balance)
- Rangoli patterns (both types)
- Mandalas (high rotational order)
Understanding rotational symmetry reveals hidden patterns in designs and nature!
