Exercise 12.2
1. In the figure, if AB = CD and ∠AOB = 90°, find ∠COD.
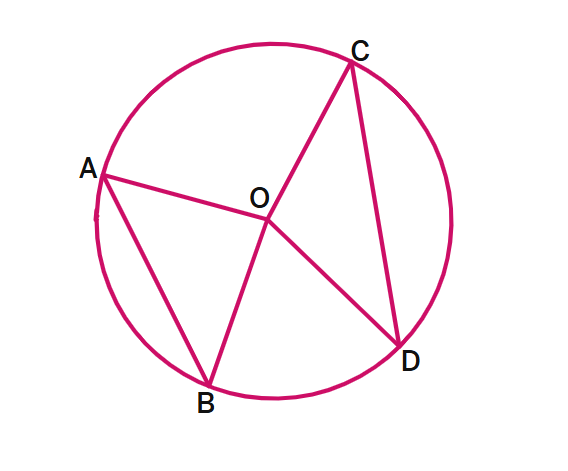
Solution:
Given: AB = CD and ∠AOB =
Since AB and CD are equal chords of the same circle:
Equal chords subtend
Therefore: ∠AOB =
Since ∠AOB = 90°:
∠COD =
2. In the figure, PQ = RS and ∠QRS = 48°. Find ∠OPQ and ∠ROS.
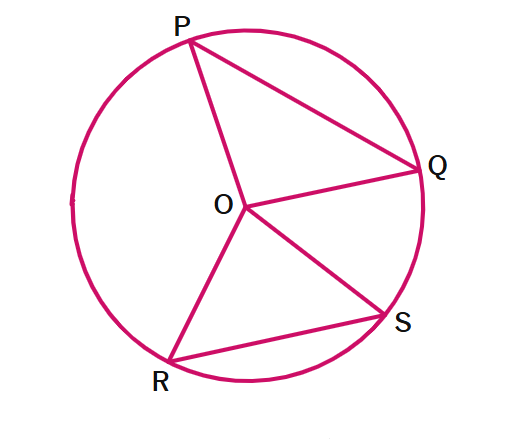
Solution:
Given: PQ = RS and ∠QRS =
Since PQ = RS (equal chords):
Equal chords subtend
Therefore: ∠POQ =
Since ∠QRS is an inscribed angle and ∠ROS is the central angle subtending the same arc RS:
Central angle =
∠ROS = 2 × ∠QRS = 2 ×
Since ∠POQ = ∠ROS:
∠POQ =
In triangle OPQ, OP = OQ (
So triangle OPQ is
∠OPQ = ∠OQP = (180° - ∠POQ)/2 = (180° -
3. In the figure PR and QS are two diameters. Is PQ = RS?
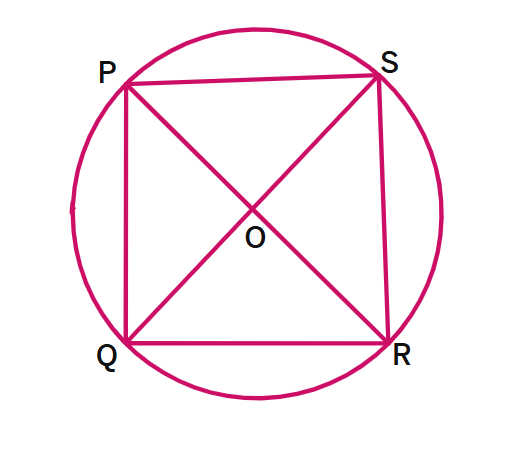
Solution:
Given: PR and QS are
Since both are diameters, they pass through the
In the circle:
PO = OR =
QO = OS =
All radii of a circle are
PO = QO = RO = SO =
In triangles POQ and ROS:
PO =
QO =
∠POQ =
By
Therefore: PQ =
Answer: Yes, PQ = RS
