Exercise 6.5
1. PQR is a triangle, right-angled at P. If PQ = 10 cm and PR = 24 cm, find QR.
Solution:
Given: PQ = 10cm, PR = 24cm
Let QR be x cm.
triangle PQR
In right angled triangle QPR,
By Pythagoras Theorem,
x =
Thus, the length of QR is 26 cm.
2. ABC is a triangle, right-angled at C. If AB = 25cm and AC = 7 cm, find BC.
Solution:
Given: AB = 25cm, AC = 7cm
Let BC be x cm.
triangle ABC
In right angled triangle ABC,
By Pythagoras Theorem,
x =
Thus, the length of BC is 24 cm.
3. A 15 m long ladder reached a window 12 m high from the ground on placing it against a wall at a distance a. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall.
15 m long ladder
Solution:
Let AC be the ladder and A be the window.
Given: AC = 15m, AB = 12m
Let CB be a m.
triangle ABC
In right angled triangle ABC,
By Pythagoras Theorem,
x =
Hence, the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall is 9 m.
4. Which of the following can be the sides of a right triangle?In the case of right-angled triangles, identify the right angles.
a
(i) 2.5 cm,6.5 cm, 6 cm.
Solution:
Let us consider, the larger side be the hypotenuse and also using Pythagoras theorem:
In △ABC,
triangle ABC
We have: L.H.S =
R.H.S =
Thus, L.H.S = R.H.S.
Therefore, the given sides form a right angled triangle.
Right angle lies on the opposite to the greater side 6.5cm i.e. at
b
(ii) 2 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm.
Solution:
Let us consider, the larger side be the hypotenuse and also using Pythagoras theorem:
LHS =
RHS =
Thus, LHS
Therefore, the given sides do not form a right angled triangle.
c
(iii) 1.5 cm, 2cm, 2.5 cm.
Solution:
Let us consider, the larger side be the hypotenuse and also using Pythagoras theorem:
triangle PQR
In △PQR,
LHS =
RHS =
Since, LHS = RHS
Therefore, the given sides form a right angled triangle.
Right angle lies on the opposite to the greater side 2.5cm i.e. at
5. A tree is broken at a height of 5 m from the ground and its top touches the ground at a distance of 12 m from the base of the tree.Find the original height of the tree.
Solution:
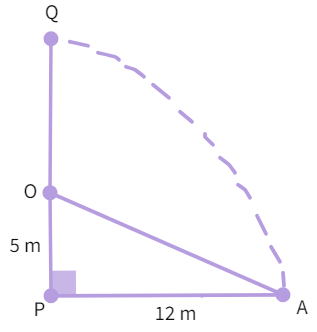
- Let the tree be represented by PQ where PQ is the original height and is broken at point O with the end touching the ground at A. Thus, PO =
m and PA = m - Substituting for PO and PA
- Calculating squares
- Adding
- Finding square root, we get
- Since, OA = OQ as the part of the tree no longer vertically standing.
- Substituting
- Adding to get final value to be
m. - Hence PQ = 18 m
6. Angles Q and R of a ∆PQR are 25° and 65°. Write which of the following is true:
triangle ABC
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Solution:
We know that, sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
∠P + ∠Q + ∠R = 180°
∠P +
∠P +
∠P = 180° - 90°
∠P =
Thus, triangle PQR is a right angled at
As one of the angles is 90° that means it is a right-angled triangle and the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
Therefore, by Pythagoras theorem,
Here, Perpendicular =
Hence, option (ii) is correct.
7. Find the perimeter of the rectangle whose length is 40 cm and a diagonal is 41 cm.
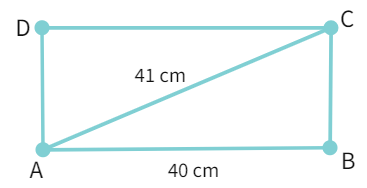
Solution:
- Let the rectangle be ABCD, where length AB = 40 cm and AC i.e. the diagonal = 41 cm. In right triangle ABC, we have, let the rectangle be ABCD, where length AB = 40 cm and AC i.e. the diagonal = 41 cm. So by Pythagoras property
- Substituting
- Calculating squares
- Simplifying
- Subtracting:
BC 2 - Finding square root, we get: BC =
- The perimeter P of ABCD
- Substituting
- Calculating sum: P =
cm - Hence P = 98 cm
8. The diagonals of a rhombus measure 16 cm and 30 cm. Find its perimeter.
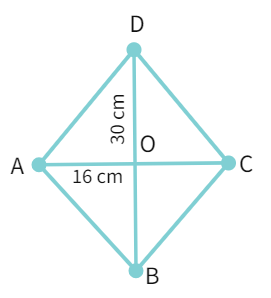
Solution:
- Let ABCD be a rhombus whose diagonals intersects each other at O. Since, the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at 90°, ∆OAB and the other 3 triangles are right anlged triangles. Consider ∆OAB and pythagoras theorem we have.
- Since, the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at 90°, OA = OC =
cm and OB = OD = cm. Substituting. - Calculating squares
- Adding, we get
- Finding square root, we get:
- Since all sides are equal in a rhombus, the perimeter of rhombus ABCD
- Replacing AB value with calculated value.
- Multiplying, we get the final value of perimeter to be
cm. - Hence perimeter = 68 cm.
