Area of a Quadrilateral
Any quadrilateral can be divided into two
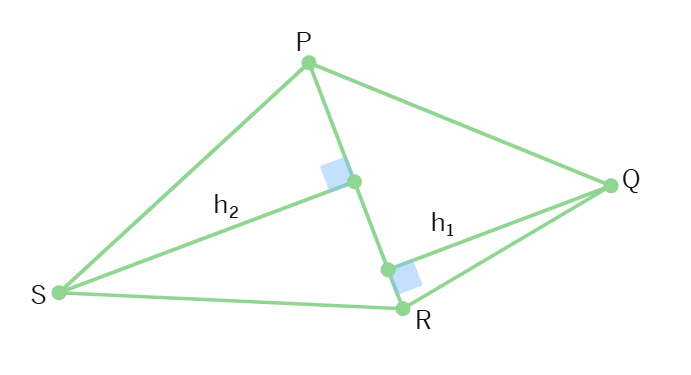
Consider quadrilateral PQRS:
Draw diagonal PR to split it into two triangles
From points Q and S, draw perpendicular lines to PR
Let's call these heights h₁ and h₂ respectively
Let's call the diagonal length 'L'
Thus, we have:
Area of triangle PQR =
Area of triangle RSP =
Total area of PQRS =
This can be written as:
Area =
