Exercise 9.1
2. Find the area enclosed by each of the following figures
(i).
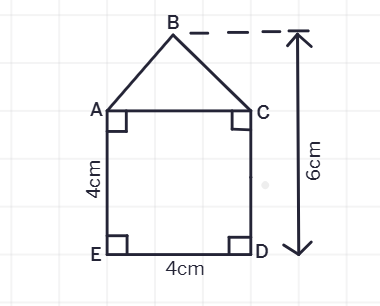
Solution:
The figure can be divided into two parts: a square and a triangle.
The side of the square is
Area of the square = side × side
Area of the square = 4 cm × 4 cm
Area of the square =
The base of the triangle is the same as the side of the square, which is 4 cm.
The height of the triangle is the difference between the total height and the side of the square: 6 cm - 4 cm =
Area of the triangle = (
Area of the triangle = (
Area of the triangle =
Total area = Area of the square + Area of the triangle
Total area =
Total area =
Therefore, the total area enclosed by the figure is 20
(ii).
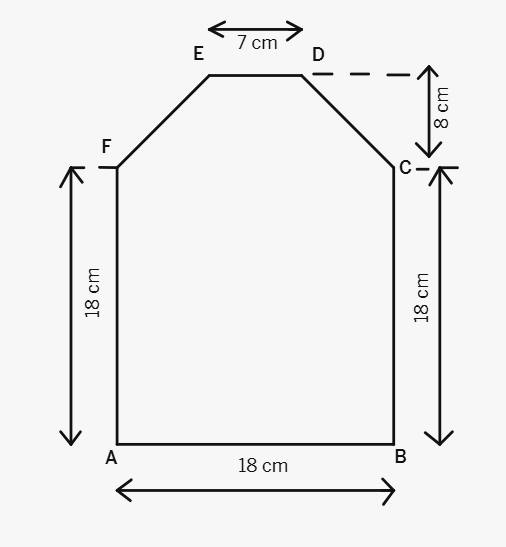
Solution:
The figure can be divided into three parts: a rectangle and two trapeziums.
Area of the rectangle = length × width
Area of the rectangle =
Area of the rectangle =
Area of one trapezium = (
Parallel sides of the trapezium are 7 cm and 18 cm, and the height is 5 cm.
The height is found by subtracting the length of the rectangle from the total height.
18 cm + 8 cm =
=
Then divide by 2 since there are two trapezoids,
However, the picture shows 8cm total height, so the height of the trapezoid is 8cm - 3cm =
Area of one trapezium = (
Area of one trapezium = (
Area of one trapezium =
Since there are two trapeziums, the total area of the trapeziums is 2 × 62.5
Total area of the figure = Area of the rectangle + Area of the two trapeziums
Total area of the figure = 324
Total area of the figure =
Therefore, the total area enclosed by the figure is 449
(iii).
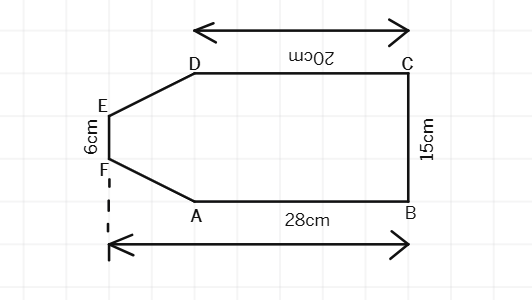
Solution:
The figure can be divided into three parts: a rectangle and two trapeziums.
Area of the rectangle = length × width
Area of the rectangle =
Area of the rectangle =
Area of one trapezium = (
Parallel sides of the trapezium are 6 cm and 20 cm, and the height is
Area of one trapezium = (
Area of one trapezium = (
=
Since there are two trapeziums, the total area of the trapeziums is 2 × 52
Total area of the figure = Area of the rectangle + Area of the two trapeziums
Total area of the figure = 300
Total area of the figure =
Therefore, the total area enclosed by the figure is 384
3. Calculate the area of a quadrilateral ABCD when length of the diagonal AC = 10 cm and the lengths of perpendiculars from B and D on AC be 5 cm and 6 cm respectively.
Solution:
Given: Diagonal AC =
Perpendicular from B to AC =
Perpendicular from D to AC =
The area of quadrilateral ABCD can be calculated as the sum of the areas of two triangles, ABC and ADC.
Area of triangle ABC = (
Area of triangle ABC = (
Area of triangle ABC = (
Area of triangle ABC =
Area of triangle ADC = (
Area of triangle ADC = (
Area of triangle ADC = (
Area of triangle ADC =
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of triangle ABC + Area of triangle ADC
Area of quadrilateral ABCD =
Area of quadrilateral ABCD =
Therefore, the area of quadrilateral ABCD is 55
4. Diagram of the adjacent picture frame has outer dimensions 28 cm × 24 cm and inner dimensions 20 cm × 16 cm. Find the area of the shaded part of the frame, if the width of each section is the same.
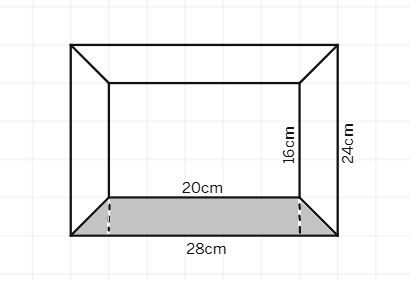
Solution:
Area of the outer rectangle =
Area of the inner rectangle =
Area of the shaded part of the frame = Area of outer rectangle - Area of inner rectangle.
Area of the shaded part of the frame = 672
Area of the shaded part of the frame =
Therefore, the area of the shaded part of the frame is 352
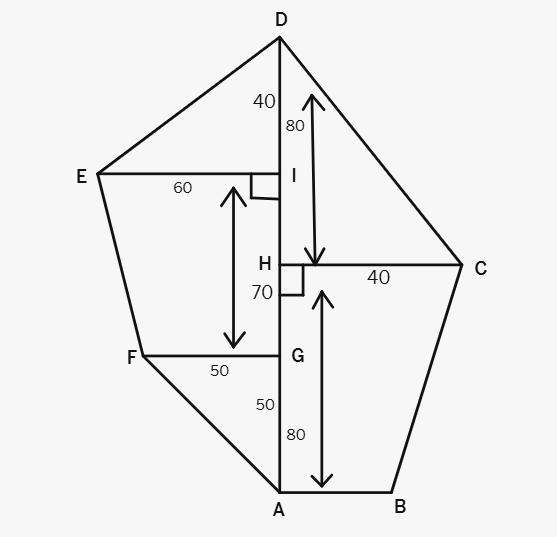
5. Find the area of the field.
Solution:
Divide the shape into triangles and rectangles.
Triangle ADE: (
Triangle ABF: (
Rectangle: 40 × 40 =
Triangle BCD: (
Triangle EFC: (
Total: 1200 + 1250 + 1600 + 800 + 400 =
6. The ratio of the length of the parallel sides of a trapezium is 5:3 and the distance between them is 16cm. If the area of the trapezium is 960
Solution:
Let the lengths of the parallel sides be
Distance between parallel sides (height) =
Area of trapezium =
Area of trapezium = (
960 = (
960 = (
960 =
x =
x =
Length of first parallel side = 5x = 5 × 15 =
Length of second parallel side = 3x = 3 × 15 =
Therefore, the lengths of the parallel sides are 75 cm and 45 cm.
7. The floor of a building consists of around 3000 tiles which are rhombus shaped and each of its diagonals are 45 cm and 30 cm in length. Find the total cost of flooring if each tile costs rupees 20 per
Solution:
Given: Number of tiles =
Diagonal 1 (
Diagonal 2 (
Cost per
Area of one rhombus tile = (
Area of one rhombus tile = (
Area of one rhombus tile =
Total area of 3000 tiles = 3000 × 675
Total area of 3000 tiles =
Convert
Total area in
Total area in
Total cost of flooring = Total area in
Total cost of flooring = 202.5
Total cost of flooring = Rs.
Therefore, the total cost of flooring is Rs. 4050.
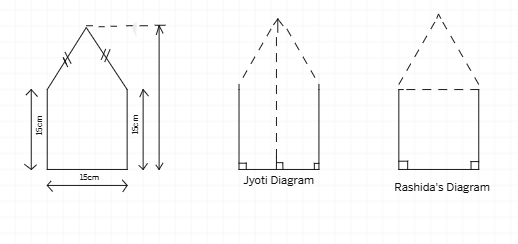
8. There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in figure. For finding its area Jyothi and Rashida divided it in two different ways. Find the area in both ways and what do you observe?
Solution:
Jyothi's Diagram:
Jyothi divides the pentagon into a square and a triangle.
Square Area:
Side = 15 cm
Area = side × side = 15 cm × 15 cm =
Triangle Area:
Base = 15 cm
Height = 15 cm
Area = (
Total Area (Jyothi's): 225
Rashida's Diagram:
Rashida divides the pentagon into two congruent trapezoids.
Trapezoid Area:
Parallel sides: 15 cm and 15 cm
Height =
Area = (
Total Area (Rashida's): 112.5
There is an error in Rashida's calculation. The total area should be the same in both methods.
Let's correct Rashida's method:
Trapezoid Area:
Parallel sides: 15 cm and 15 cm
Height =
Area = (
Total Area (Rashida's): 112.5
The error in Rashida's method was that she only calculated the area of one trapezoid.
Corrected Total Area (Rashida's): 225
The area of the pentagon is 337.5
