Exercise 9.2
1. A rectangular acrylic sheet is 36 cm by 25 cm. From it, 56 circular buttons, each of diameter 3.5 cm have been cut out. Find the area of the remaining sheet.
Solution:
Given: Length of rectangular sheet =
Width of rectangular sheet =
Number of circular buttons =
Diameter of each button =
Area of rectangular sheet = length × width
Area of rectangular sheet =
=
Radius of each circular button =
Radius of each circular button = (
Area of one circular button = π ×
Area of one circular button = π ×
=
=
Total area of 56 circular buttons =
=
Area of remaining sheet = Area of rectangular sheet - Total area of circular buttons
Area of remaining sheet = 900
Area of remaining sheet =
2. Find the area of a circle inscribed in a square of side 28 cm.
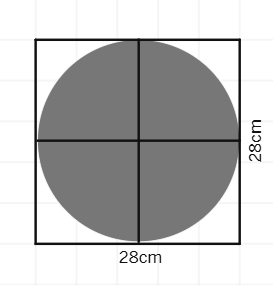
[Hint. Diameter of the circle is equal to the side of the square]
Solution:
When a circle is inscribed in a square, the diameter of the circle is equal to the side length of the square.
Given: Side length of the square =
Therefore, the diameter of the circle =
Radius of the circle (r) =
Area of the circle (A) = π ×
A = π ×
A = π ×
Using π =
A = 22 ×
A =
_Therefore, the area of the circle is 616
3. Find the area of the shaded region in the figure.
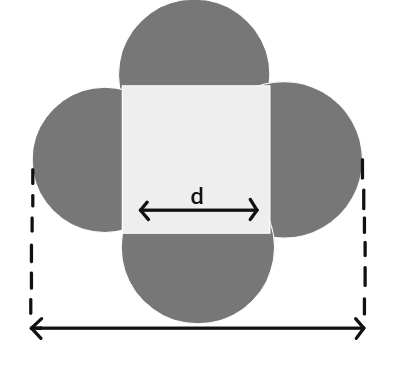
Solution:
Given: Side of the square (d) =
The shaded region consists of four semi-circles.
Diameter of each semi-circle = Side of the square = 21 cm.
Radius of each semi-circle (r) =
Area of one semi-circle = (
= (
= (
Area of four semi-circles =
=
Area of four semi-circles =
Using π ≈
Area =
Therefore, the area of the shaded region is 693
ii.
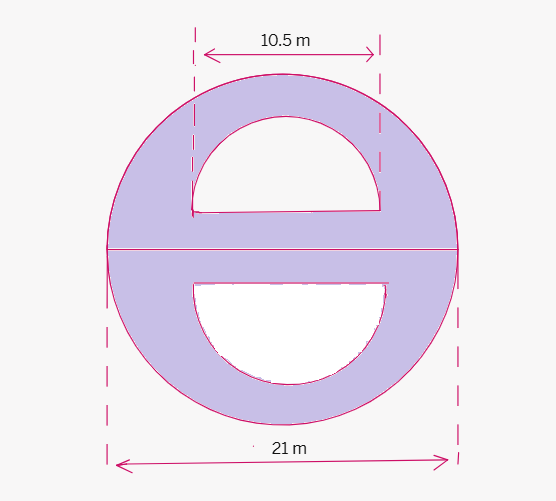
Solution:
Given: Diameter of the outer circle =
Radius of the outer circle (R) =
Diameter of the inner semi-circles =
Radius of the inner semi-circles (r) =
Area of the outer circle = π ×
Area of one inner semi-circle = (
Area of two inner semi-circles = 2 × 13.78π
Area of the shaded region
Area of the shaded region = 110.25π
Using π ≈ 3.14159: Area = 82.68 × 3.14
Area =
_Therefore, the area of the shaded region is approximately 259.87
4. The adjacent figure consists of four small semi-circles of equal radii and two big semi-circles of equal radii (each 42 cm). Find the area of the shaded region.
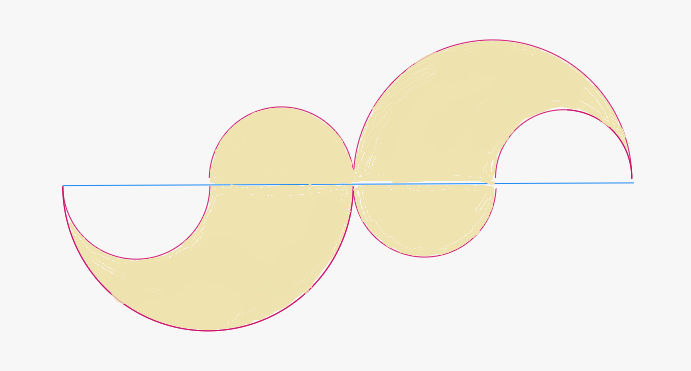
Solution:
Given: Radius of each big semi-circle (R) =
From the figure, the diameter of the big semi-circle is equal to the
Therefore, the diameter of each small semi-circle = Radius of the big semi-circle =
Radius of each small semi-circle (r) =
The shaded regions are the difference between the big semi-circles and the small semi-circles.
Area of one big semi-circle = (
Area of two big semi-circles = 2 × 882 π
Area of one small semi-circle = (
Area of four small semi-circles = 4 × 220.5π
We need to find the difference between the area of the two big semi-circles and the area of the four small semi-circles.
Shaded Area = Area of two big semi-circles - Area of four small semi-circles = 1764π
Using π ≈ 22/7: Shaded Area = 882 × (
However, we need to consider only the visible shaded regions.
The visible shaded regions are the difference between the large semi-circles and the corresponding small semi-circles.
The area of one big semi-circle minus the area of two small semi-circles is:
Since there are two sets, the total shaded area is: 2 × 441π =
Using π =
The area of the shaded portion is the difference between the big semi-circles and the corresponding small semi-circles.
Area of the shaded portion = 2 × (Area of big semi-circle - Area of small semi-circle)
Area of the shaded portion = 2 × (
Using π =
Therefore, the area of the shaded region is 4158
5. The adjacent figure consists of four half circles and two quarter circles. If OA = OB = OC = OD = 14 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
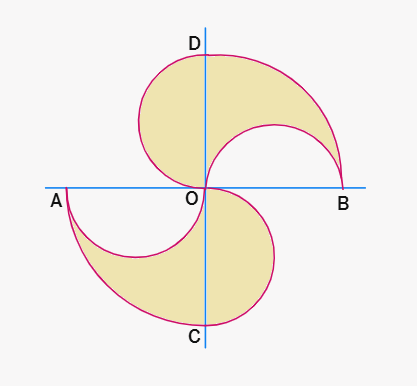
Solution:
Given: OA = OB = OC = OD =
Radius of each semi-circle and quarter circle (r) =
The shaded region consists of two quarter circles and the difference between two semi-circles.
Area of one quarter circle = (
Area of two quarter circles = 2 × 49π
Area of one semi-circle = (
The shaded area is the sum of two quarter circles and the difference between the areas of two semi-circles.
The difference between the two semi circles is actually
Therefore, the shaded area is equal to the area of the two quarter circles.
Shaded area =
Using π =
Shaded area =
Therefore, the area of the shaded region is 308
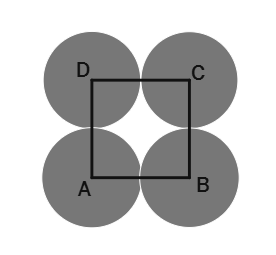
6. In the adjacent figure A, B, C and D are centres of equal circles which touch externally in pairs and ABCD is a square of side 7 cm. Find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
Given: Side of the square ABCD =
The circles touch externally, so the distance between their centres is equal to the
The side of the square is equal to the
Therefore, the diameter of each circle =
Radius of each circle (r) =
Area of the square ABCD =
The shaded region is formed by the area of the square minus the area of four quarter circles.
Area of one quarter circle = (
Area of four quarter circles = 4 × 3.0625π
Area of the shaded region = Area of the square ABCD - Area of four quarter circles.
Area of the shaded region = 49
Using π ≈
Area = 49
Area =
_Therefore, the area of the shaded region is 10.5
7. Find the area inside the equilateral triangle not included in the circles.
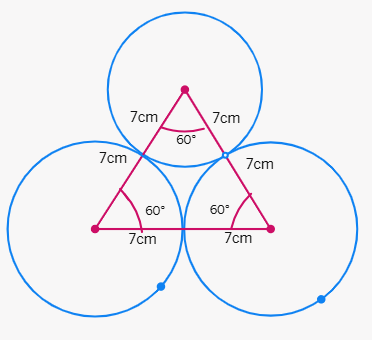
Solution:
Determine the Triangle Side:
We are given that the area of the equilateral triangle is
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is (
So, (
Solving for
Determine the Circle Radius:
The radius of each circle is half the side length of the triangle.
Therefore, the radius (r) =
Determine the Sector Area:
Each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°.
The area of a sector is (
Area of one sector = (
Determine the Total Sector Area:
There are three sectors, so the total sector area is 3 × (
5. Determine the Shaded Area:
The shaded area is the area of the triangle minus the total sector area.
Shaded area =
Using π =
Shaded area = 49 ×
Shaded area =
Shaded area =
_Therefore, the area of the portion in the triangle not included in the circles is approximately 7.87
8. (i). Four equal circles, each of radius ‘a’ touch one another. Find the area between them.
Solution:
The centers of the four circles form a square with side length 2a.
Area of the square =
Area of one quadrant of a circle =
Area of four quadrants =
Area between the circles = Area of square - Area of four quadrants
Area between the circles =
(ii) Four equal circles are described about the four corners of a square so that each circle touches two of the others. Find the area of the space enclosed between the circumferences of the circles, each side of the square measuring 24 cm.
Solution:
Side of the square =
Radius of each circle =
Area of the square =
Area of one quadrant of a circle = (
Area of one quadrant of a circle = (
Area of four quadrants = 4 × 36π
Area enclosed between the circles = Area of square - Area of four quadrants
Area enclosed between the circles = 576
= 576
= 576
SolutionArea enclosed between the circles =
9. From a piece of cardboard, in the shape of a trapezium ABCD, with AB || CD and ∠BCD = 90°, a quarter circle is removed. Given AB = BC = 3.5 cm and DE = 2 cm, calculate the area of the remaining piece of the cardboard. (Take π to be
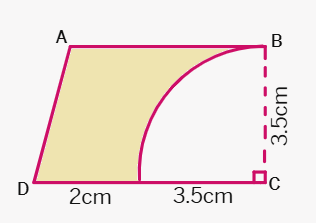
Solution:
Given:
AB =
BC =
DE =
∠BCD =
Since AB || CD and ∠BCD = 90°, ABCD is a
CD = DE + EC = DE + AB (since ABCE is a
Area of trapezium ABCD = (
The removed part is a quarter circle with radius BC =
Area of the quarter circle = (
Area of the remaining piece of cardboard = Area of trapezium ABCD - Area of the quarter circle.
Area of the remaining piece = 15.75
_Therefore, the area of the remaining piece of cardboard is 6.125
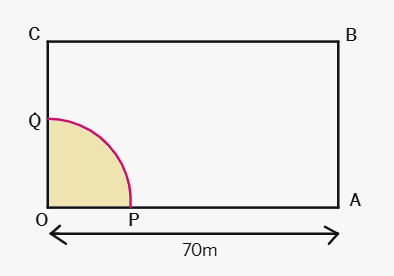
A horse is placed for grazing inside a rectangular field 70 m by 52 m and is tethered to one corner by a rope 21 m long. How much area can it graze?
Solution:
The horse can graze a quarter-circle area.
Given: Rope length (radius) =
Area of a full circle = π ×
Area of a quarter-circle =
Area = (
Area = (
Area = (
Area = (
Area =
Therefore, the horse can graze 346.5
